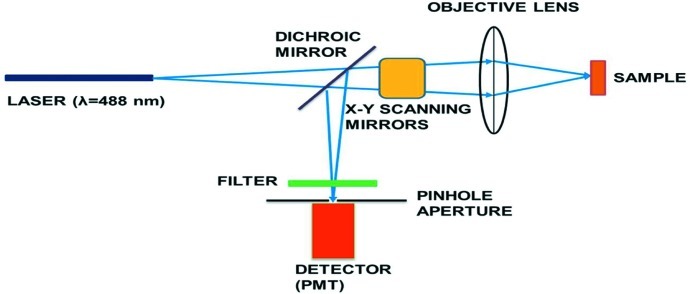
Figure 1.
Schematic of a typical confocal microscopy system. A laser beam passes through a dichroic mirror and is focused on the sample after going through xy scanning galvanometer mirrors. The light from the illuminated focal point in the sample follows the same optical path back (conventionally known as epi detection) but is diverted via a dichroic mirror and an optional optical filter into the photomultiplier tube (PMT) for detection. A pinhole aperture of about the size of the Airy disc placed at the conjugate image plane before the detector acts to reject out-of-focus and scattered light.