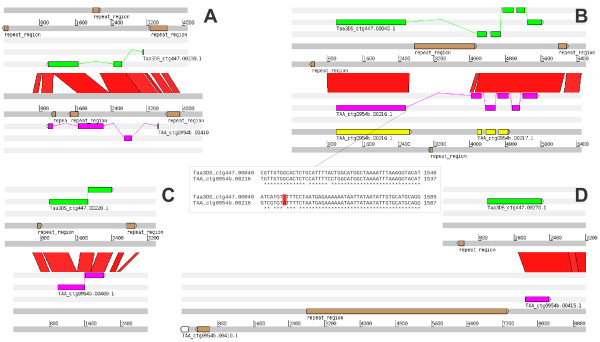
Figure 2.
Comparison of gene – pseudogene homoeologous pairs. Intact coding sequences (all from the 3DS locus) are in upper trace highlighted in green colour. Pseudogenes (from 3B locus) are displayed in the lower trace in pink. Sequence features shown in brown represent repetitive elements. Red connections between traces represent Blastn hits between sequences. A) Insertion of repetitive element into the last exon of TAA_ctg0954b.00410 gene caused its pseudogenization. B) Pseudogene TAA_ctg0954b.00216 was originally annotated as two different gene fragments (yellow features). Comparison with the orthologous 3DS gene allowed their annotation as one pseudogene. Sequence alignment revealed insertion of single nucleotide causing frame shift (sequence cut-out). Remaining two genes TAA_ctg0954b.00400 ( C) and TAA_ctg0954b.00415 ( D) lost their function by partial deletion. While inner deletion disrupted gene TAA_ctg0954b.00400 ( C), 5' end of TAA_ctg0954b.00415 ( D) was removed. No homology with 3DS orthologous gene Taa3DS_ctg447.00270.1 was found upstream to closest gene (leftmost feature in white).