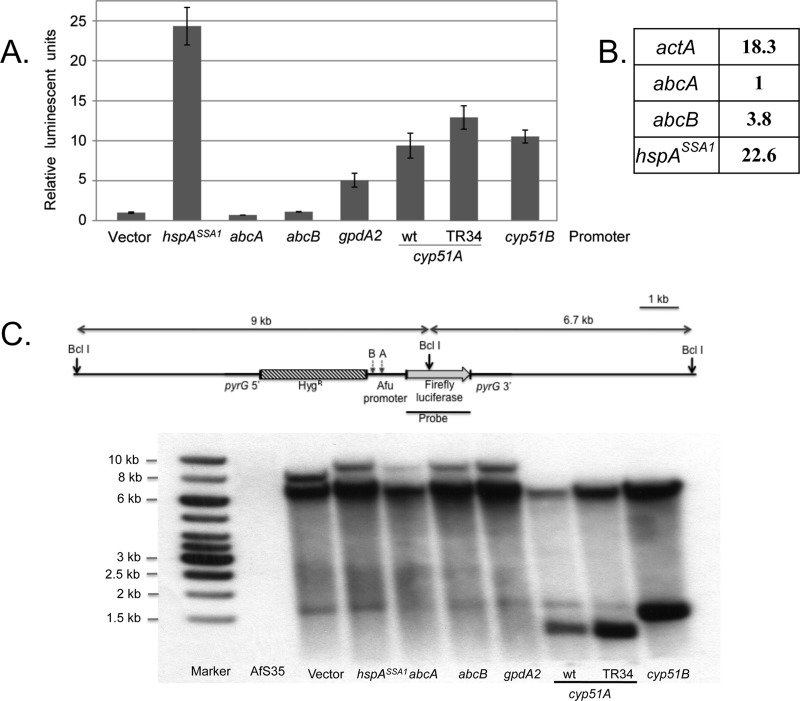
Fig 2.
Characterization and validation of luciferase fusion genes. (A) All luciferase fusion genes were integrated at the pyrG locus in the AfS35 strain (akuAΔ). Transformants were grown to mid-log phase, and protein extracts were prepared and assayed for levels of luciferase activity as described above. Enzyme activities were normalized to the level produced in the absence of an inserted A. fumigatus promoter (Vector). Inserted promoters included hspASSA1, corresponding to the A. fumigatus homologue of the ScSSA1 Hsp70-encoding gene; abcA and abcB are two A. fumigatus homologues of ABC transporter ScPDR5; gpdA2 encodes an A. fumigatus glyceraldehyde-3-dehydrogenase isoform, cyp51A and cyp51B are the genes encoding the lanosterol 14α demethylase, while TR34 indicates the presence of a 34-bp duplication in the cyp51A promoter associated with azole resistance. (B) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of transcripts from the Af293 strain was carried out using total RNA and the indicated gene-specific primers. Transcript levels were normalized to those from the abcA gene. (C) Southern blot analysis to confirm single-copy targeted integration of the fusion promoter constructs at the pyrG locus. Genomic DNA was digested with BclI, which cuts once within the firefly luciferase gene, and also within the cyp51A and cyp51B promoters. The relative positions of the BclI restriction sites present in either cyp51A (A) or cyp51B (B) are indicated. The probe was prepared from the indicated segment of the luciferase gene. The expected DNA fragment sizes upon single integration at pyrG are indicated along the lanes. A nonspecific, cross-hybridizing DNA fragment is also seen around 1.5 kb.