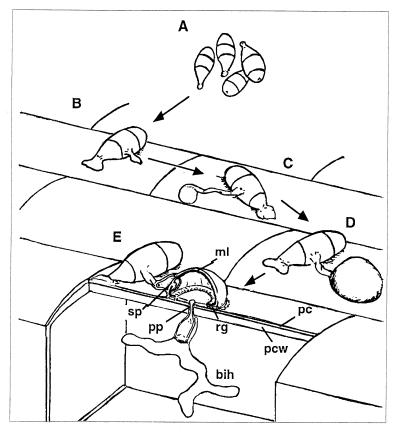
Figure 1.
Penetration of host leaves by the rice blast fungus. (A) Conidia are disseminated in water drops splashing from a sporulating lesion. (B) A strong glue sticks conidia to the host surface. (C) Appressorium differentiates rapidly after conidium germination. (D) Mature appressorium is a melanized, dome-shaped and thick-walled cell. (E) Penetration peg breaches the plant cuticle and cell wall by mechanical force. After penetration, a bulbous infection hypha invades the epidermal cell. Abbreviations: ml, melanin layer; sp, septum; pp, penetration peg; rg, ring of conidial glue; bih, bulbous infection hypha; pc, plant cuticle; pcw, plant cell wall.