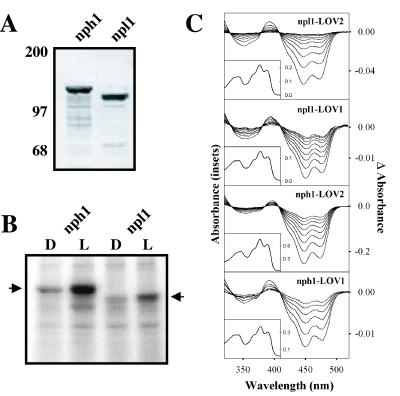
Figure 1.
Biochemical and photochemical properties of Arabidopsis npl1. (A) Western blot analysis of nph1 and npl1 expressed in insect cells. Soluble protein fractions prepared from insect cells expressing either nph1 or npl1 were probed with anti-His antibody. Positions of molecular mass markers are indicated on the left in kilodaltons. (B) Autoradiograph showing the in vitro light-dependent phosphorylation of soluble protein fractions prepared from insect cells expressing either nph1 or npl1 (indicated by arrows). All manipulations were carried out under dim red light. Samples were given a mock irradiation, D, or irradiated with white light, L, at a total fluence of 30,000 μmol⋅m−2. Arrows on the left and right indicate the approximate molecular masses of recombinant nph1 and npl1 (125 kDa and 110 kDa, respectively). (C) Absorption spectra (Insets) and light-minus-dark difference spectra (main panels) of oat nph1 and Arabidopsis npl1 expressed and purified from E. coli. The difference spectra show dark recovery to the ground state after a light flash and were taken at 1-s intervals after the light flash, except for nph1 LOV2, for which the time interval was 5 s.