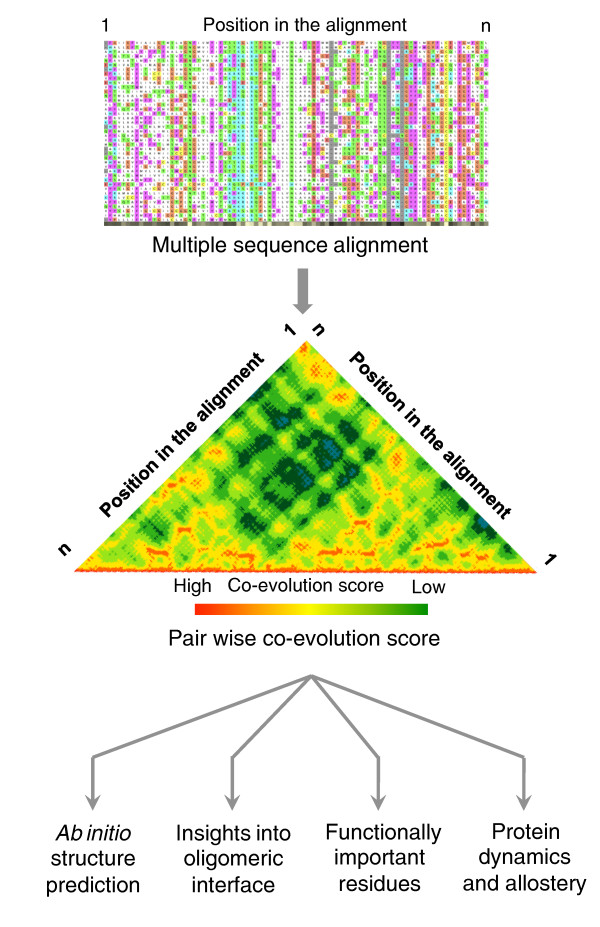
Figure 1.
Inferring protein structure, function and dynamics from residue co-evolution. Co-evolving positions within a sequence can be inferred from investigating multiple sequence alignment of homologous protein sequences (Box 1). Such information can be exploited to provide information on spatial proximity of residues and hence to infer three-dimensional structures, residues at the oligomeric interface, amino acids that are functionally important and the presence of potential allosteric communication paths in the structure.