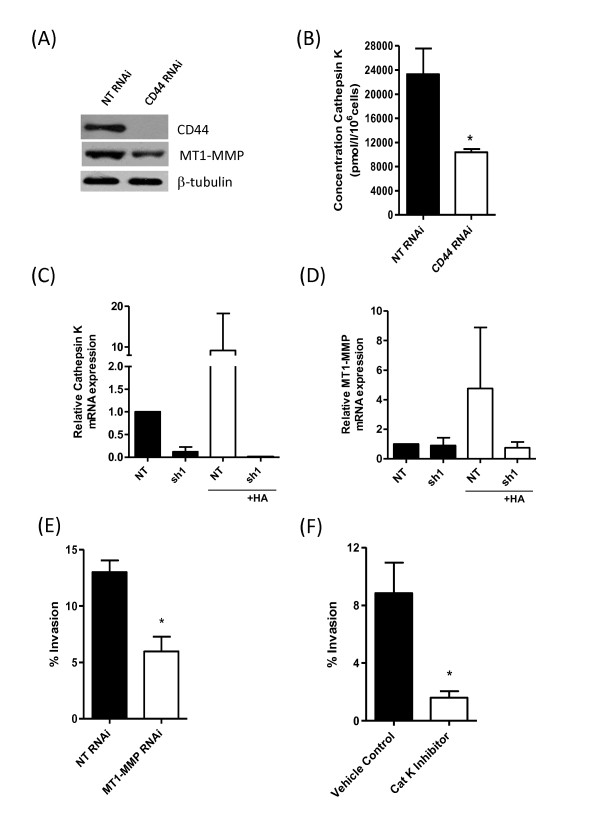
Figure 7.
CD44 regulates MT1-MMP and cathepsin K expression to underpin BL-BCa cell invasion. (A) Immunoblot showing reduced MT1-MMP protein expression on transfection of MDA-MB-231Hi cells with a CD44-targeted RNAi SMARTPool relative to a nontargeting oligonucleotide-transfected cell population. (B) Bar graph demonstrating the impact of CD44 knockdown on the secretion of cathepsin K by MDA-MB-231Hi cells. Cathepsin K concentration was reduced from 23,310 ± 4,227 pmol/L/106 cells in NT cells to 10,380 ± 526.7 pmol/L/106 cells in CD44-depleted cells (P < 0.05; n = 4). (C) Bar graph comparing the mRNA transcript levels for cathepsin K in MDA-MB-231 NT and MDA-MB-231 sh#1 cells, in the absence and presence of an exogenous HA stimulus (100 μg/ml). (D) Bar graph comparing the mRNA transcript levels for MT1-MMP in MDA-MB-231 NT and MDA-MB-231 sh#1 cells, in the absence and presence of an exogenous HA stimulus (100 μg/ml). (E) Bar graph illustrating the effect of RNAi-mediated suppression of MT1-MMP in MDA-MB-231Hi cells on their invasion through collagen I. (F) Bar graph showing the effect of administering a pharmacologic inhibitor of cathepsin K on the invasion of MDA-MB-231Hi cells through a collagen I matrix. Statistically significant differences between data points in quantitative assays were determined by using a Student two-tailed t test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.