Figure 6.
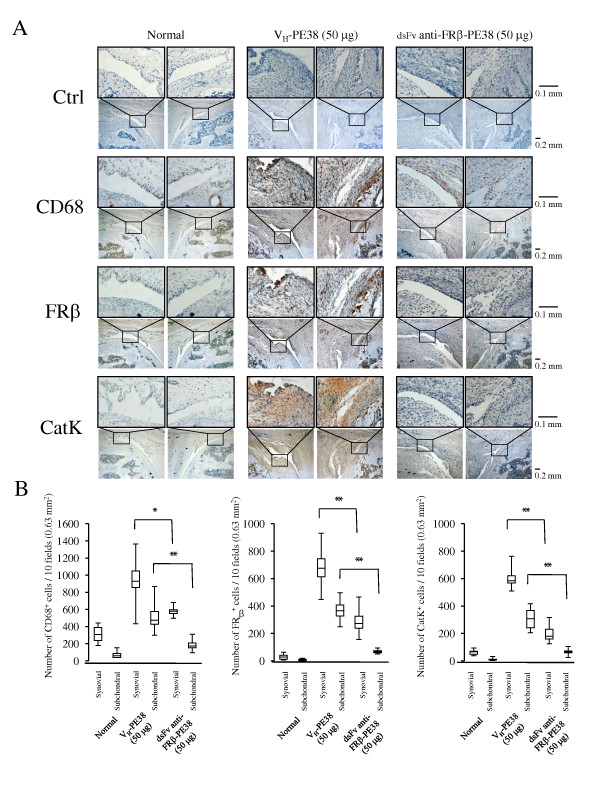
CD68-, FRβ-, and cathepsin K-positive cells in the knee joints of AIA rats treated using an anti-FRβ immunotoxin. (A) Knee joints from normal rats and AIA rats treated with 50 µg of VH-PE38 or dsFv anti-FRβ-PE38 were stained with isotype-matched controls (a mixture of mouse IgG1 and IgM mAbs, and rabbit IgG), antibodies against CD68, FRβ, or cathepsin K, and positive cells were counted. Photographs are representative of negative control and CD68-, FRβ-, and cathepsin K-positive cells in the knee joints of eight rats per group. Note that the synovium from AIA rats treated using dsFv anti-FRβ-PE38 showed fewer CD68-, FRβ-, and cathepsin K-positive cells compared to those treated using VH-PE38. Original magnifications were ×100 and ×400. (B)Numbers of CD68-, FRβ-, and cathepsin K-positive cells were counted in the knee joints of each group. Data from eight rats per group are presented as box plots, where the boxes represent the 25th to 75th percentiles, the lines within the boxes represent the median, and the lines outside the boxes represent the 10th and 90th percentiles. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 compared to the group treated using VH-PE38. AIA, antigen-induced arthritis; FRβ, folate receptor β; Ig, immunoglobulin.
