Figure 4.
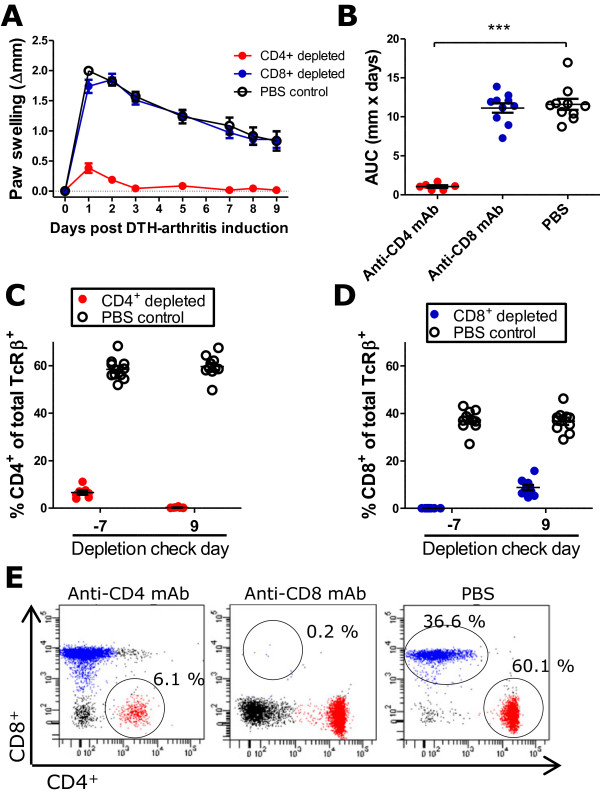
The delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH)-arthritis inflammatory response is dependent on CD4+ T cells. The response is dependent on CD4+ cells and independent of CD8+ cells, as demonstrated by the failure of mice depleted of CD4+ cells to develop a paw swelling response and the ability of mice depleted of CD8+ cells to develop a paw swelling response no different than that of the phosphate-buffered saline (PBS)-treated control group. (a) Paw swelling measured over days 0 to 9 after DTH-arthritis induction. Mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) is shown (n = 6 to 10 per group). (b) Area under the curve (AUC) of paw swelling based on paw swelling data from days 0 to 9 after arthritis induction. Mean ± SEM is shown (n = 6 to 10 per group). ***P ≤ 0.001. (c) Percentage of CD4+ cells of total T-cell receptor-beta-positive (TCRβ+) cells measured on days -7 and 9 after DTH-arthritis induction shown for mice receiving anti-CD4 monoclonal antibody (mAb) or PBS on days -8 and -1. The data show that CD4+ cells were efficiently depleted. Cells were gated on CD45 and TCRβ. Mean ± SEM is shown (n = 6 to 10 per group). (d) Percentage of CD8+ cells of total TCRβ+ cells measured on days -7 and 9 after DTH-arthritis induction shown for mice receiving anti-CD8 mAb or PBS on days -8 and -1. The data show that CD8+ cells were efficiently depleted. Cells were gated on CD45 and TCRβ. Mean ± SEM is shown (n = 6 to 10 per group). (e) Representative flow cytometry plots from the depletion check on day -7 demonstrating the efficiency of the depleting mAbs. Cells were gated on CD45 and TCRβ. The circled populations represent the remaining percentage of either CD4+ or CD8+ cells of total TCRβ+ cells.
