Fig 1.
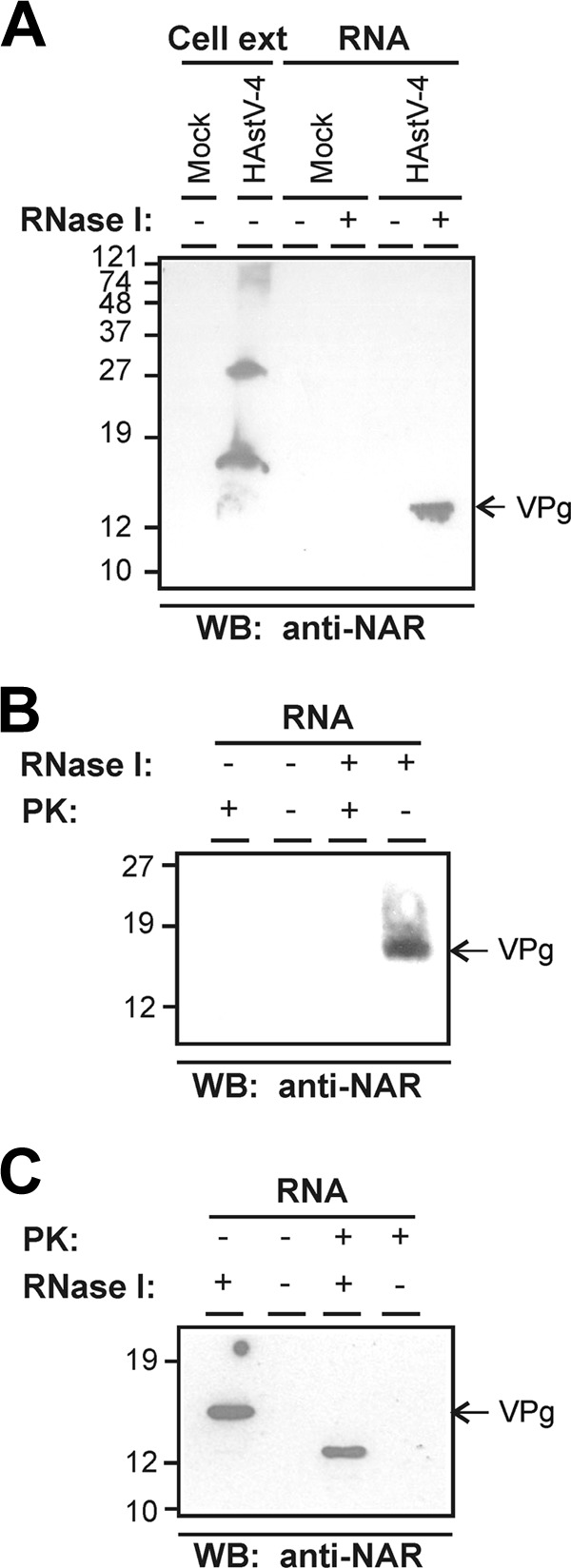
Identification of a viral protein covalently associated with HAstV RNA. (A) Western blotting (WB) analysis of HAstV-4-infected CaCo2 cell extracts and proteins that were copurified with RNA isolated from mock-infected and infected cells at 24 h postinfection and stained with anti-NAR antiserum. RNA-copurified proteins were analyzed before and after treatment with RNase I. (B) Proteolytical digestion of the RNA-associated protein was evaluated by incubation with proteinase K (PK). RNA samples purified from infected cells were mock treated or treated first with RNase I and subsequently incubated with or without PK. Complete digestion of the 13- to 15-kDa protein was confirmed by WB using the anti-NAR antibody. (C) Susceptibility of the VPg protein to PK digestion before the RNase I treatment. Samples treated first with PK and second with RNase I were analyzed by WB with the anti-NAR antibody. Molecular size marker positions in kilodaltons (kDa) are indicated on the left of each panel. Slight mobility pattern differences between the VPg protein after RNase treatment in panels A, B, and C may be explained by the erratic electrophoretic mobility of disordered proteins and/or the efficiency of the RNase treatment.
