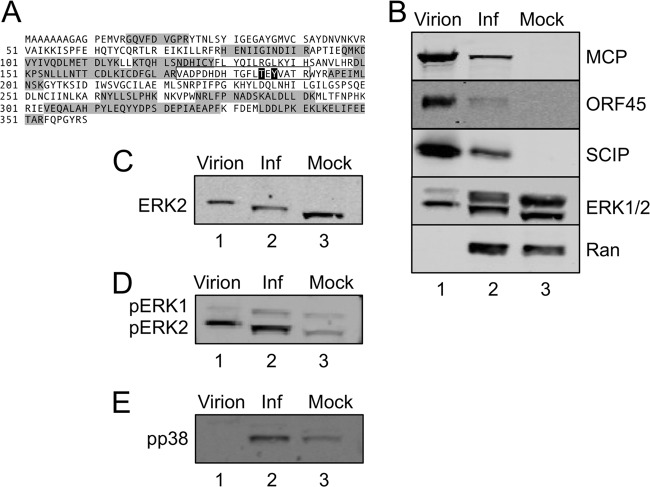
Fig 1.
Preferential incorporation of ERK2 into RRV particles. (A) MS and MS/MS analyses of sucrose gradient-purified RRV particles identified multiple tryptic peptides (shaded) that mapped to ERK2. MS/MS analysis of these samples following titanium enrichment identified a single ERK2 phosphopeptide (boxed sequence, with the phosphorylated residues [threonine 185 and tyrosine 187] in white with black outlining). These sites are the known MEK-specific target sites. (B) Supernatants and cell pellets from RRV-infected RhF were harvested at 72 h p.i., virions were formed into pellets and then gradient purified from the supernatant (lane 1), and whole-cell lysates from the RRV-infected RhF (Inf; lane 2) and mock-infected RhF (Mock; lane 3) were immunoblotted for viral structural proteins MCP, ORF45, and SCIP, as indicated, as well as for total ERK (ERK1/2). The cellular protein Ran served as a loading control for the cellular extracts (lanes 2 and 3). (C) The blots presented in panel B were stripped and reprobed for ERK2 to confirm its position on the immunoblot. (D) The blots presented in panel B were stripped and reprobed with an antibody that specifically recognizes diphosphorylated/activated (pT185/pY187) ERK1/2 to confirm the MS data. (E) The blot presented in panel B was also stripped and reprobed for another activated (nuclear) MAPK, phospho-p38 (pp38).