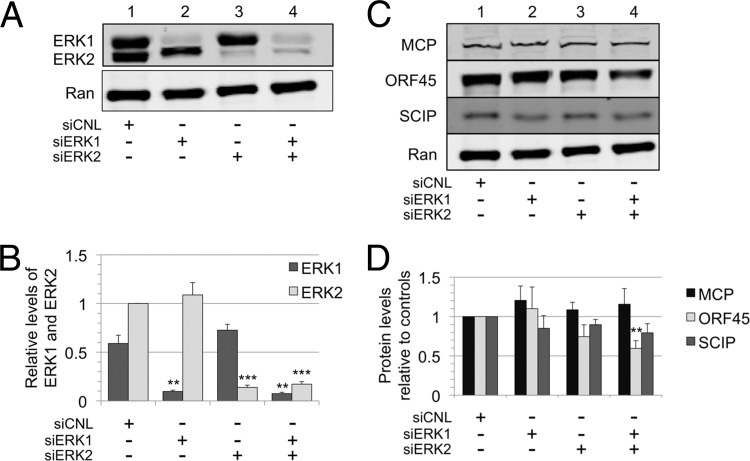
Fig 5.
Differential suppression of ERK1 and ERK2 isoforms only minimally affects intracellular viral protein production. (A) RhF were transfected with nontargeting siRNA (siCNL), siERK1, siERK2, or siERK1 plus siERK2, as indicated. At 24 h posttransfection, cells were infected with RRV. Cells were harvested at 48 h p.i., and immunoblots of cell lysates were probed for total ERK (upper panel) as well as Ran to normalize for loading differences (lower panel). The quantitative immunoblot is from a representative experiment. (B) Graphical representation of the expression of each ERK isoform relative to its level in cells treated with siCNL. The ERK2 value was set at 1.0. Data represent the means ± SEM of the results of four separate experiments. P values were determined using Student's t test, comparing the level under the experimental condition to the control level for the corresponding ERK isoform. The values in columns lacking asterisks were not statistically distinguishable from corresponding siCNL values. With siERK1, the P value for ERK1 was 0.0013; with siERK2, the P value for ERK2 was 0.0001; and with siERK1 plus siERK2, the P values for ERK1 and ERK2 were 0.001 and 0.0001, respectively. (C) Cell lysates from the same four siRNA conditions were also probed with antibodies to viral proteins MCP, ORF45, and SCIP as well as to Ran, as indicated. (D) Changes in the expression of the viral proteins presented in panel C compared to that of CNL are represented graphically. Data represent the means ± SEM of the results of the same four separate experiments described for panel B. With siERK1 plus siERK2, the P value for ORF45 was 0.0064. The other levels were not statistically different from control values.