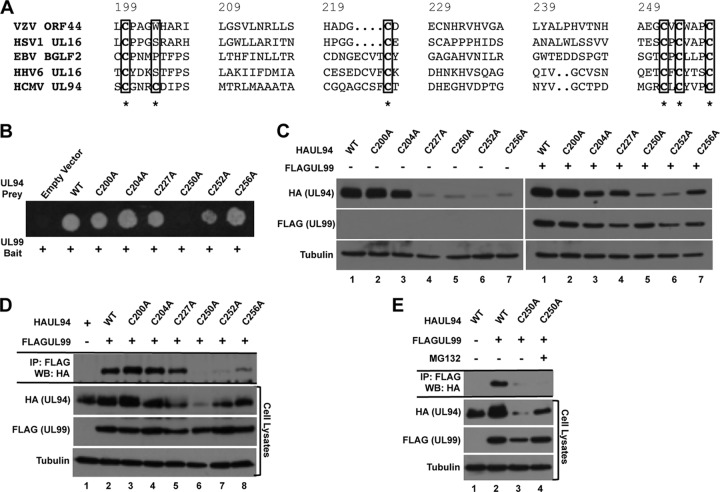
Fig 3.
Mapping UL94 interaction domains. (A) Amino acid sequence alignment of residues 200 to 256 of HCMV UL94 with its homologs in varicella-zoster virus (VZV), herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV1), Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), and human herpesvirus 6 (HHV6). Cysteine residues that were mutated to alanine for mapping studies are indicated with an asterisk. (B) Yeast cells were cotransformed with bait plasmid expressing wild-type (WT) UL99 and prey plasmid expressing wild-type UL94 or the indicated UL94 mutant. Interactions were assessed by growth of cotransformed cells on medium lacking histidine. (C) 293T cells were transfected with plasmid DNA expressing the indicated HAUL94 alone (left) or with FLAGUL99 (right). Total protein was harvested at 48 h posttransfection, and levels of UL94 and UL99 were analyzed by Western blotting. (D) 293T cells were cotransfected with plasmid DNA expressing the indicated HAUL94 and FLAGUL99. Total protein was harvested at 48 h posttransfection, and immunoprecipitation was performed with anti-FLAG antibody. Immune complexes were separated by SDS-PAGE, and Western blotting was performed with anti-HA antibody. (E) 293T cells were cotransfected with plasmid DNA expressing the indicated HAUL94 and FLAGUL99 and treated with MG132 for 9 h prior to protein harvest, as indicated. Total protein was harvested at 48 h posttransfection, and immunoprecipitation was performed with anti-FLAG antibody. Immune complexes were separated by SDS-PAGE, and Western blotting was performed with anti-HA antibody.