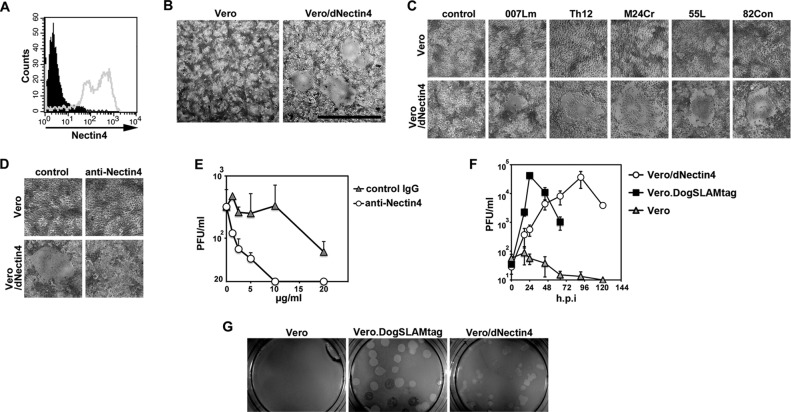
Fig 1.
Infection of Vero/dNectin4 cells with CDV. (A) Vero/dNectin4 (gray empty profile) and parental Vero (filled black profile) cells were stained with a goat anti-human nectin4 polyclonal antibody (R&D Systems), followed by staining with Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated anti-goat IgG. (B) Vero/dNectin4 (right panel) and parental Vero (left panel) cells were infected with the Ac96I strain. At 48 h postinfection, the cells were observed under a phase-contrast microscope. Bar, 1 mm. (C) Vero/dNectin4 (lower panels) and parental Vero (upper panels) cells were infected with wild-type strains of CDV (007Lm, Th12, M24Cr, 55L, or 82Con) or left uninfected (control). At 48 h postinfection, the cells were observed under a phase-contrast microscope. (D) Vero/dNectin4 (lower panels) and parental Vero (upper panels) cells were infected with the wild-type Ac96I CDV strain in the presence (anti-Nectin4) or absence (control) of the goat anti-human nectin4 polyclonal antibody. At 48 h postinfection, the cells were observed under a phase-contrast microscope. (E) Vero/dNectin4 cells pretreated with increasing concentrations of anti-Nectin4 antibody or control IgG were infected with 1,000 PFU of strain Ac96I and cultured with the same concentrations of the antibody or control IgG. At 48 h postinfection, the virus titers of the supernatants were determined in plaque assays. (F) Vero/dNectin4, Vero.DogSLAMtag, and parental Vero cells were infected with the wild-type Ac96I CDV strain at a multiplicity of infection of 0.05. At various time intervals, the virus titers were determined in plaque assays. (F) Vero/dNectin4 (right panel), Vero.DogSLAMtag (middle panel), and the parental Vero (left panel) cells in 12 well-cluster plates were infected with the wild-type Th12 strain and overlaid with medium containing 1% agarose. At 7 days postinfection, the plaques were observed under a stereoscope.