Figure 2.
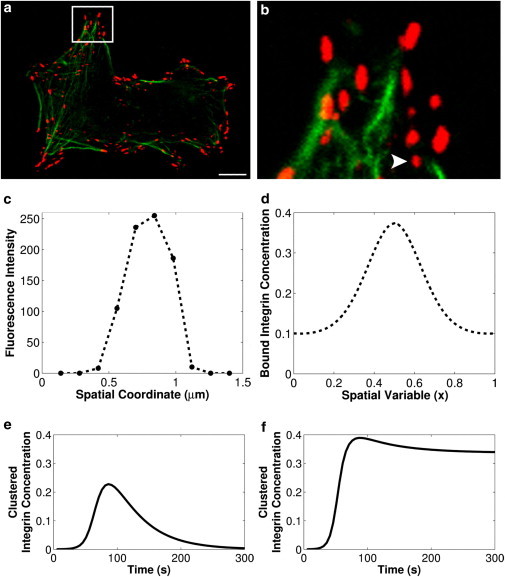
Comparison of measured bound integrin concentration and simulated bound integrin concentration. (a) Confocal microscope image of adherent cells showing bound integrin (red, color online), and actin cytoskeleton (green, color online). Scale bar is 10 μm. (b) Higher magnification of the portion of the cell indicated in panel a; (arrow) nascent integrin cluster analyzed in panel c. (c) Example concentration profile of bound integrin in the nascent integrin cluster indicated in panel b. (d) Simulated bound integrin concentration, calculated as [B] = [IE] + [IET] + [IETK]. The simulation was initiated with a small pulse of active talin at x = 0.5 ([T]∗o = 0.001) as the nucleation event; model parameter values are as given in Table 1. (e and f) Dynamics of integrin cluster formation and turnover under conditions representing: (e) cluster turnover (k5r = 1 s−1) and (f) cluster stabilization (k5r = 0).
