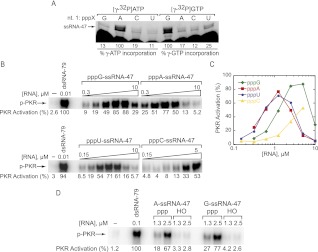
FIGURE 2.
All ssRNA-47 5′-triphosphate-starting nucleotides activate PKR. (A) Verification of starting nucleotide identity. RNA was transcribed from DNA templates coding for starting the transcript with pppG, pppA, pppC, and pppU, in the presence of [γ-32P]ATP or [γ-32P]GTP. The expected starting RNA nucleotide based on template (nt. 1: pppX) is indicated. Percent incorporation was calculated by normalizing the counts at the indicated mobility “ssRNA-47” to the counts from the pppA lane for [γ-32P]ATP incorporation, or the pppG lane for [γ-32P]GTP incorporation. 7 M urea gel is shown. (B) Activation of PKR by ssRNA-47 with pppG, pppA, pppU, and pppC. RNA concentrations were 0.31, 0.63, 1.3, 2.5, 5.0, and 10 μM for pppG- and pppA-ssRNA-47; 0.15, 0.31, 0.63, 1.3, 2.5, 5.0, and 10 μM for pppU-ssRNA-47; and 0.15, 0.31, 0.63, 1.3, 2.5, and 5.0 μM for pppC-ssRNA-47. Phosphorylation activities are provided under the gels and were normalized to the dsRNA-79 lane in the top gel. (C) Graphical representation of phosphorylation activities from panel B as a function of RNA concentration. (D) Activation of PKR by A-ssRNA-47 and G-ssRNA-47 are both dependent on a 5′-triphosphate. RNAs starting with 5′-triphosphate were generated by in vitro T7 transcription, while RNAs starting with 5′-OH-G and 5′-OH-A were chemically synthesized. Phosphorylation activities are provided under the gel and were normalized to the dsRNA-79 lane. For both panels B and D, 10% SDS-PAGE gels are shown, with the position of phosphorylated PKR (p-PKR) indicated.