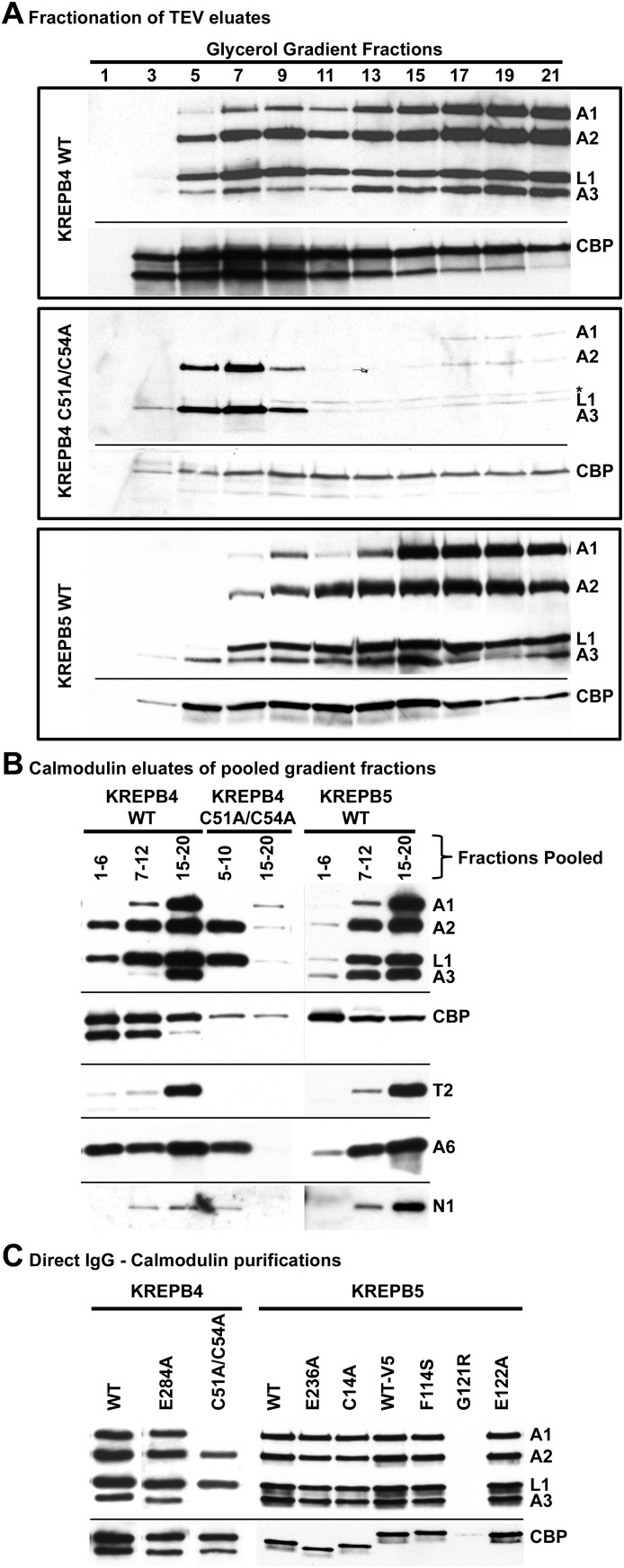
FIGURE 3.
Western analyses of TAP isolated complexes using tagged KREPB4 or KREPB5. (A) Western analyses of 10%–30% glycerol gradient fractions of TEV eluates for KREPB4 wild-type (top panel), KREPB4 C51A/C54A mutant (middle panel), and KREPB5 wild-type (bottom panel) that were simultaneously probed with monoclonal antibodies against KREPA1, KREPA2, KREL1, and KREPA3 (top part in each panel) to show editosome components. The same blots were also probed with anti-CBP antibody (bottom part in each panel) to show tagged KREPB4 or KREPB5. Note the KREPB4 C51A/C54A mutant predominantly purifies a subcomplex of ∼10S. (B) Western analyses of complexes from pooled gradient fractions (indicated) that were further purified by calmodulin affinity. Blots were probed for editosome components KREPA1, KREPA2, KREL1, KREPA3, KRET2, KREPA6, and KREN1. (C) Western analyses of complexes sequentially purified by placing TEV eluates directly onto calmodulin affinity resin. These calmodulin eluates were used in subsequent editing activity assays. Note that the G121R mutation to KREPB5 substantially prevents copurification of other editosome proteins. Variation in the size of tagged proteins in anti-CBP Western results from the presence or absence of Myc-His or V5 epitopes.