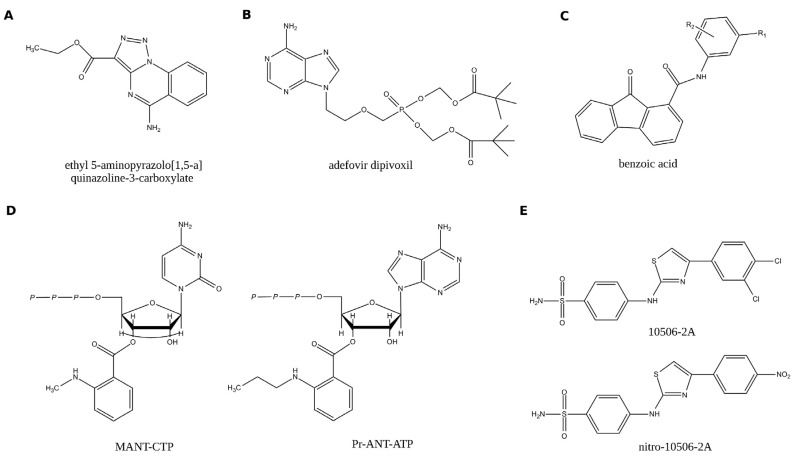
Figure 2.
Examples of potent inhibitors of EF toxin component. Inhibitors in panel A to D were identified by targeting EF active site. (A) ethyl 5-aminopyrazolo[1,5-a]quinazoline-3-carboxylate, [32]; (B) (9-[2-[[bis[(pivaloyloxy)methoxy]phosphinyl]methoxy]ethyl]adenine; or bis-POM-PMEA, [26]; (C) 3-[(9-oxo-9H-fluorene-1-carbonyl)-amino]-benzoic acid, [33,34]; (D) MANT-CTP and propyl-ANT-ATP, [35]; (E) 4-[4-(4-dichloro-phenyl)-thiazolylamino]-benzenesulfonamide (10506-2A) was first identified in a cell based assays and then selected for its ability to block EF–CaM binding. 4-[[4-(4-nitrophenyl)-2-thiazolyl] amino]-benzenesulfonamide (nitro10506-2A) was identify as a non-toxic derivative of the former [36]. They appeared to bind the helical domain of EF, thus being allosteric as the compounds of the TUA family, which will be described below (Figure 5, and ref. [37]).