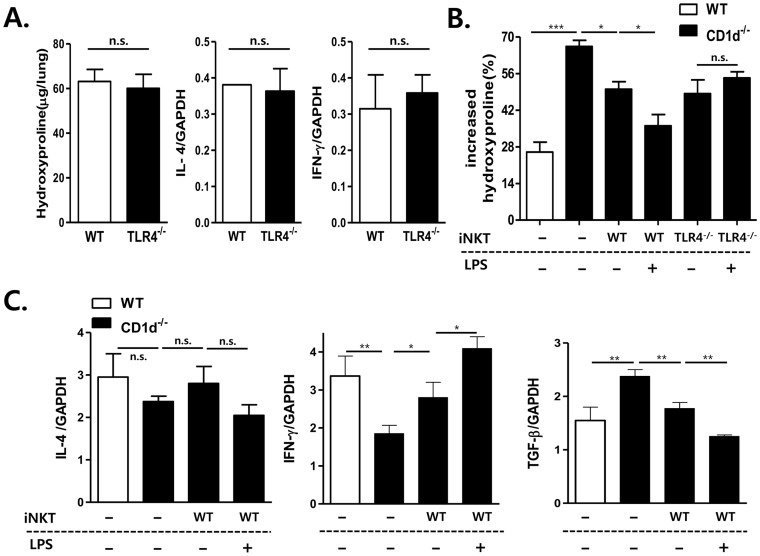
Figure 5. LPS-mediated engagement of TLR4 in iNKT cells suppresses bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis.
(A) Lungs were removed from B6 or TLR4−/− mice 7 or 21 days after an intratracheal injection of bleomycin (2 mg/kg), and the levels of hydroxyproline, and IL-4 and IFN-γ transcripts were determined. (B) Hydroxyproline content in the lungs of B6, CD1d−/−, and CD1d−/− mice adoptively transferred with sorted WT, TLR4-deficient iNKT cells, LPS-pretreated WT iNKT, or LPS-pretreated TLR4-deficient iNKT cells was determined 21 days after bleomycin injection. The increased hydroxyproline content in the lungs of experimental groups are expressed as a percentage. Data are indicated as mean ± SEM of six mice in each group. (C) The transcript levels of TGF-β1, IFN-γ, and IL-4 were determined by quantitative analysis relative to GAPDH using real-time PCR in the lungs of B6, CD1d−/−, and CD1d−/− mice adoptively transferred with sorted WT iNKT or TLR4-deficient iNKT cells seven days after intratracheal injection of bleomycin. Data are representative of three repeated experiments. (n = 3 in each group; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001).