Figure 5. The receptor and intracellular signal transduction mechanisms underling inhibition of proton-gated currents by WIN55,212-2.
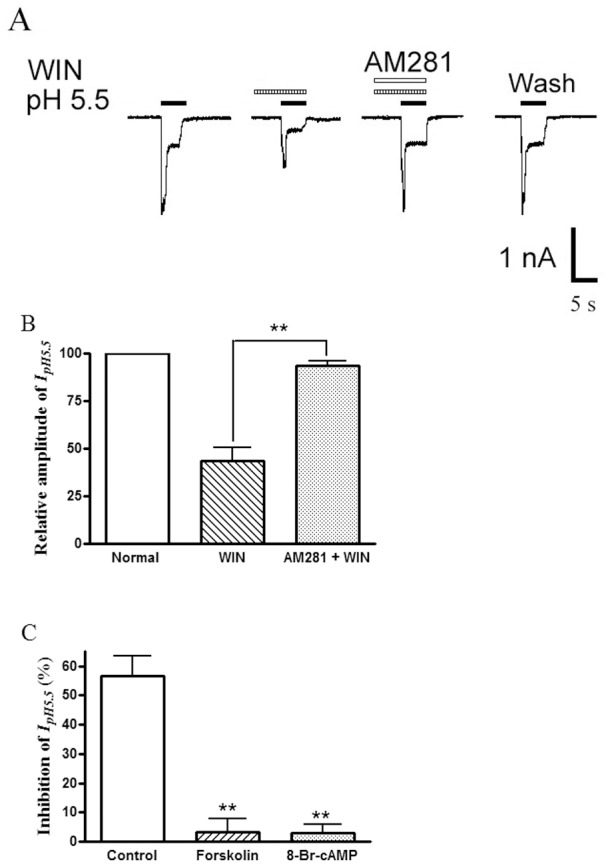
The current traces in (A) and the bar graph in (B) show that the inhibition of IpH5.5 by WIN55,212-2 (WIN, 10−7 M) pre-applied alone was abolished by the co-application of WIN55,212-2 and AM281 (10−6 M), a selective CB1 receptor antagonist **P<0.01, one way analysis of variance followed by post hoc Bonferroni’s test, n = 8. The bar graph in (C) shows the percentage decreases in the IpH5.5 induced by WIN55,212-2 (10−7 M) in control and pre-treatment of forskolin and 8-Br-cAMP conditions. The inhibition of WIN55,212-2 on proton-gated current was blocked by application of forskolin (10−5 M) or 8-Br-cAMP(10−3 M). **P<0.01, one way analysis of variance followed by post hoc Bonferroni’s test, compared with control, n = 7/each column.
