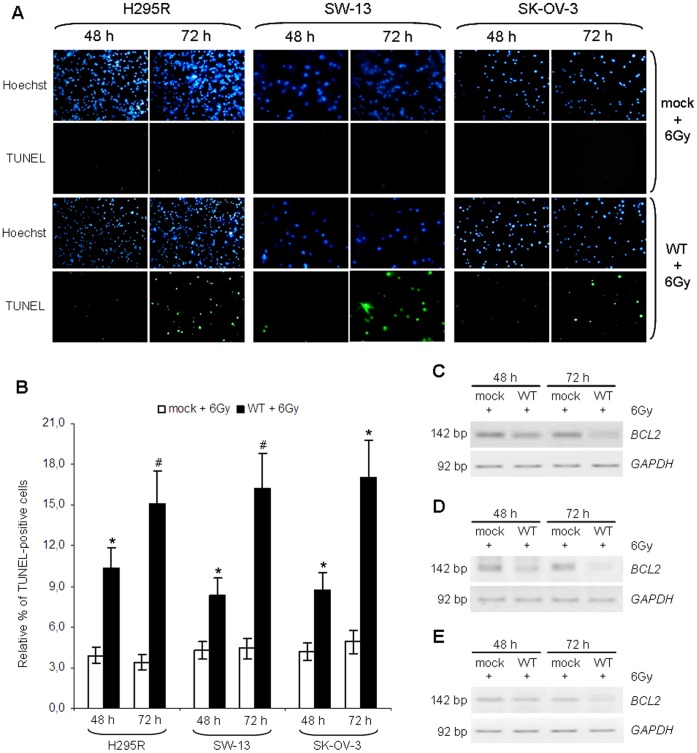
Figure 4. Induction of apoptosis by ionizing radiation following p53 stabilization.
H295R, SW-13 and SK-OV-3 cell lines were transfected with empty vector (mock) or p53-vector (WT) and irradiated at a dose of 6 Gy. (A) TUNEL assay was performed at 48 and 72 after transfection. In all cell lines, TUNEL-positive cells are detectable only in irradiated samples expressing the wild type form of TP53. Cells were also stained with Hoechst 33342 and then visualized with a fluorescence microscope at a magnification of 40×. Figure shown is representative of three experiments performed in duplicate. (B) Percentage of apoptosis in H295R, SW-13 and SK-OV-3 was calculated by comparing TUNEL-positive cells with total cells, stained with Hoechst 33342. Apoptosis increases in cells transfected with p53 vector compared with mock-irradiated samples, starting from 48 h since transfection and the effect strengthens after 72 h. (*, p<0.05; #, p<0.01). (C) BCL2 expression was evaluated in H295R cell line by RT-PCR. p53 restoration induces a significant reduction in BCL2 expression at 48 and 72 h after irradiation. (D) Inverted images relative to semi-quantitative RT-PCR analysis of BCL2 gene expression performed on SW-13 cells, showing a significant reduction in BCL2 signal in cells transfected with p53-vector following ionizing radiations treatment. (E) The effect of p53 restoration on BCL2 mRNA levels in response to irradiation was evaluated in SK-OV-3 cell lines. p53 inhibits BCL2 expression and the effect is stronger at 72 h after transfection. Images are representative of at least three independent experiments. GAPDH was used for normalization.