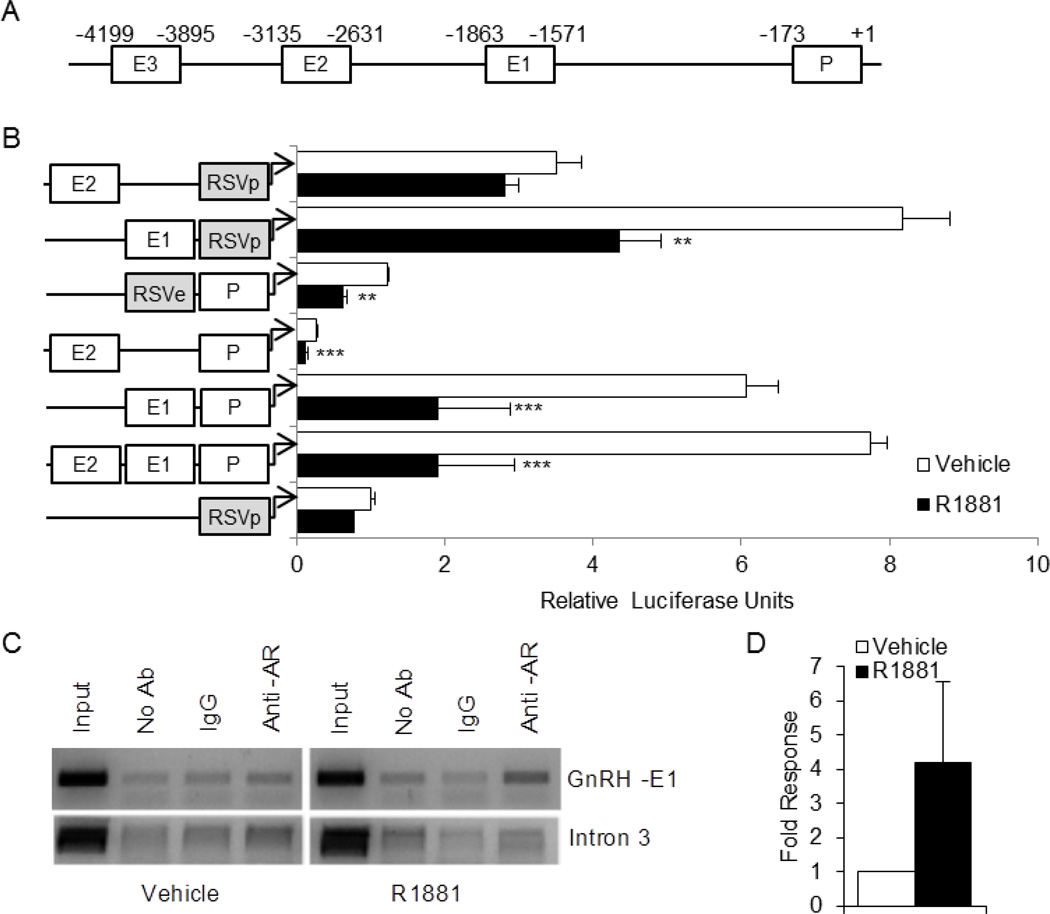
Fig. 1.
AR associates with the enhancer 1 region of the GnRH regulatory region and represses transcription. (A), Schematic of the −5 kb GnRH regulatory region, including the locations of the known enhancers and proximal promoter. (B), GT1-7 cells were transiently transfected with luciferase reporter constructs containing the GnRH-P (P), GnRH-E1 (E1), and/or GnRH-E2 (E2) regions, and/or the RSV promoter (RSVp) or enhancer (RSVe), as indicated, along with the AR expression vector. Cells were treated for 24 h with 100 nM R1881 (closed bars) or ethanol vehicle (open bars) and subjected to luciferase assay. Data are shown as relative luciferase units, relative to vehicle-treated RSVp, and represent the mean, ± SEM, of at least three experiments done in quadruplicate. **P<0.01, and ***P<0.001 versus vehicle. (B), GT1-7 cells were transiently transfected with AR and treated for 2 h with 100 nM R1881 or ethanol vehicle. Nuclei were extracted and subjected to chromatin immunoprecipitation with no antibody (no Ab), an antibody specific for AR (anti-AR), or IgG control. The resulting chromatin was analyzed by PCR with primers to GnRH-E1 or Intron 3. The gels shown were representative of three independent experiments. (C), Quantitative real time PCR was performed on the chromatin samples using primers to GnRH-E1.