Fig. 5.
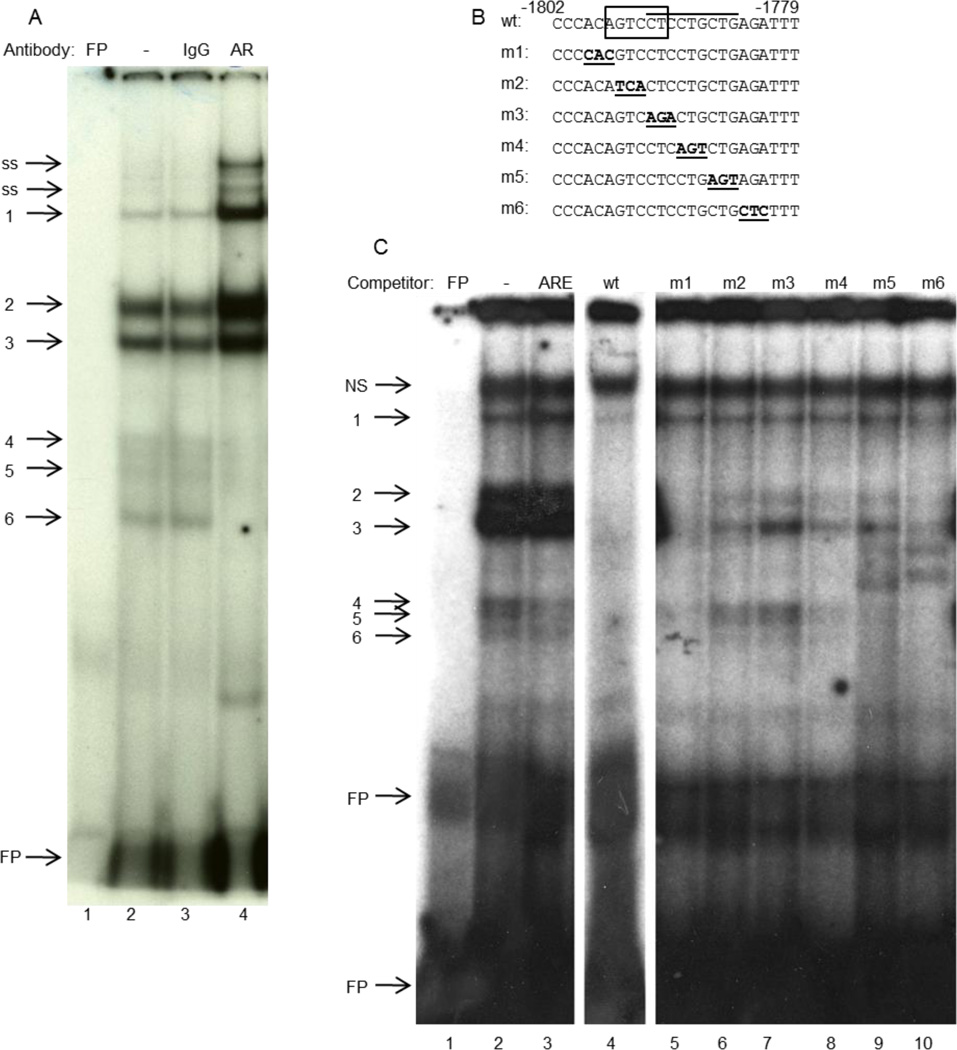
AR-containing complexes bind to the −1796/−1791 sequence of GnRH-E1. (A), Nuclear extracts from GT1-7 cells that had been transfected with AR and treated with R1881 were incubated with a radiolabeled probe containing the −1802/−1779 region of GnRH-E1, with or without antibody. Lane 1: free probe (FP); Lane 2: probe with nuclear extract; Lane 3, rabbit IgG; Lane 4, anti-AR antibody. Bands 4–6 represent AR-containing complexes; ss: super-shifted AR. (B), Sequences of the wild type (wt) and mutant oligonucleotide competitors. Box: putative HRE; overline: TPA-responsive site; bold/underline: mutations. (C), Nuclear extracts from GT1-7 cells that had been transfected with AR were incubated with a radiolabeled probe containing the −1802/−1779 region of GnRH-E1, with or without indicated unlabeled competitor. Lane 1: free probe (FP); Lane 2: probe with nuclear extract; Lane 3: unlabeled androgen response element (ARE) competitor; Lane 4: wild type (wt) unlabeled competitor; Lanes 5–10: indicated mutant unlabeled competitor. Bands 4–6 represent AR-containing complexes; NS: non-specific band.