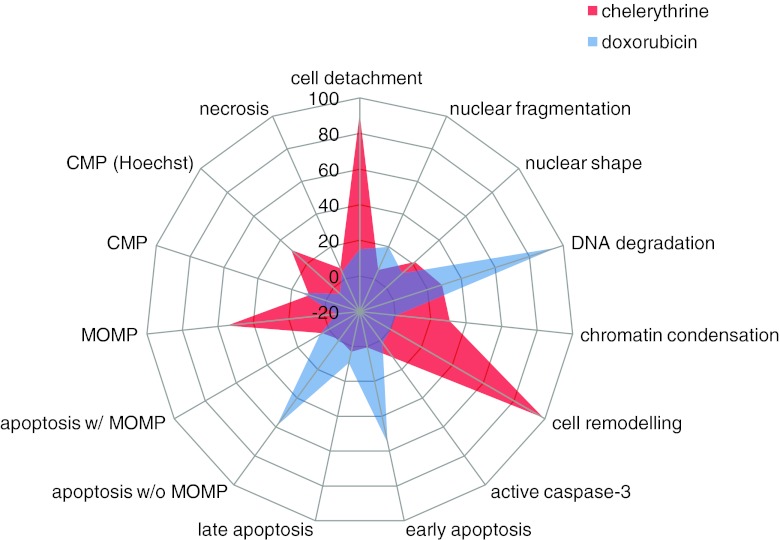
Fig. 6.
Radar chart showing multivariate chelerythrine and doxorubicin-induced cell death profiles in hiPSC-CM. Both drugs induced cardiomyocyte death but with clearly different toxicity signatures. Chelerythrine induced mitochondria dysfunction (MOMP), cell shape remodelling, chromatin condensation and moderate apoptosis and necrosis. Doxorubicin was a strong inducer of DNA degradation, early apoptosis (caspase 3 and 7 substrate without cell membrane permeabilization) with intact mitochondrial membrane potential. Axis shows cell death index, with zero representing the control. Doxorubicin: n = 22, four experiments; chelerythrine n = 12, two experiments