Figure 3. Purinergic drive does not increase with increased CO2 intensity.
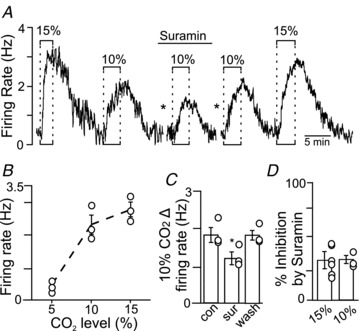
A, firing rate trace shows that exposure to 10 and 15% CO2 increased neuronal activity by 2.9 and 2.1 Hz, respectively. In the presence of suramin (100 μm), exposure to 10% CO2 increased neuronal activity only 1.6 Hz. Responsiveness to 10 and 15% CO2 was fully recovered when suramin was washed out. The asterisks denote 10 min time breaks. B, average data (n = 3) show that exposure to 10 and 15% CO2 increased neuronal activity in a relatively linear manner. C, summary data (n = 3) show that suramin decreased the firing rate response to 10% CO2. D, summary data (n = 3) show that suramin decreased the responsiveness to 10 and 15% CO2 by similar amounts, indicating that purinergic drive to chemosensitive RTN neurons does not increase in response to this range of stimulus intensities.
