Figure 4. Purinergic drive to RTN neurons is not dependent on extracellular Ca2+.
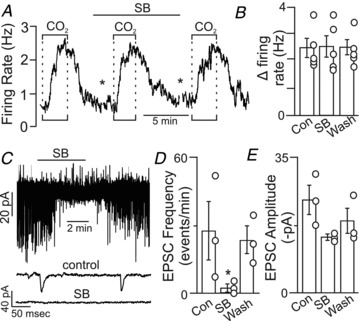
A, firing rate trace shows that the CO2/H+ sensitivity of an RTN neuron was unaffected by low Ca2+–high Mg2+ synaptic block (SB) medium. The asterisks denote 8 min time breaks. B, average data (n = 5) show that SB medium did not significantly affect CO2/H+ sensitivity (P = 0.982). C, traces of holding current (at a potential of −60 mV) show that exposure to SB medium blocked spontaneous excitatory post-synaptic currents (EPSCs) in chemosensitive RTN neurons. D and E, as expected, SB medium inhibited EPSC frequency (D, n = 3) but not EPSC amplitude (E, n = 3). Average decay time constant was 4.8 ± 0.2 ms (not shown). These results suggest that extracellular Ca2+ is not required for the purinergic drive to breathe.
