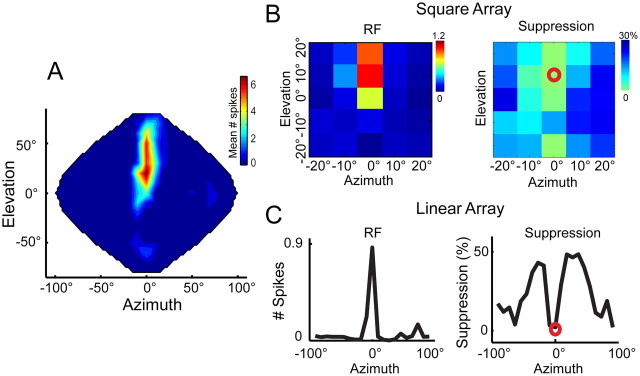
Figure 4.
Asymmetrical surround suppression in ICx. A, Full spatial RF of an ICx neuron mapped using the entire speaker array (144 speakers). The response of the neuron peaks at 0° azimuth and 10° elevation. B, SWN analysis for the same cell using the square array. Left, Spatial RF. Right, Surround effect. The red circle indicates the RF center. Suppression is stronger from the right side, which for this particular cell represents frontal space. Calibration bars indicate number of spikes per stimulus (left) and percentage suppression (right). C, The spatial RF (left) and surround effect (right) are shown for a wider range applying SWN with a linear array. Surround modulation is shown as percentage change from the mean response at the center. Similar to suppression in the square array, suppression from the right (frontal space) is greater than peripheral suppression.