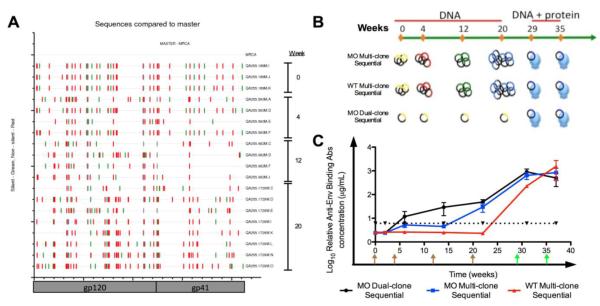
Figure 3. QA255 Env vaccine sequences, immunization approaches, and Env-specific binding antibodies.
(A) Highlighter plot illustrates accumulating non-synonymous changes in the sequence occurring longitudinally in the WT quasispecies variants incorporated in the various immunizations. Nucleotide differences from the Most Recent Common Ancestor sequence are indicated by tick marks (green, silent; red, non-silent; grey, gap). Codon location of the env gene is shown on the X-axis. Brackets to the right outline clones used for immunization on respective weeks. (B) Immunization Strategies. Rabbits were vaccinated with four either MO or WT DNA primes at weeks (brown arrows) 0, 4, 12, and 20, followed by two combination MO 1729O DNA plus LCONS protein boosts in the presence of PEI adjuvant (green arrows) on weeks 29 and 35. (C) LCONS Envelope-specific binding antibodies elicited by the immunization strategies. Relative antibody concentrations of serum samples collected two weeks after each immunization were measured by kinetic ELISA against trimeric LCONS gp140. MO Dual-clone Sequential (MO Dual-clone), black; MO Multi-clone Sequential (MO Multi-clone), blue; WT Multi-clone Sequential (WT Multi-clone), red. Dotted line represents 2.5× pre-immune titers.