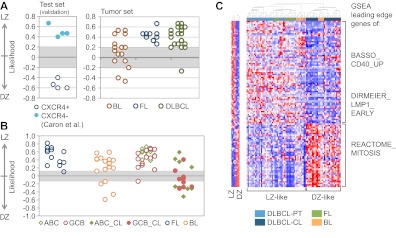
Figure 5.
Most GC-derived B-NHLs share an LZ-related phenotype. (A) Class prediction of GC-derived B-NHLs using the Weighted Voting algorithm.27 The dataset reported by Caron et al,37 where tonsillar GC B-cells were isolated according to their surface expression of CXCR4, was used as a validation set. (B) Class prediction in the same B-NHL samples using the SPLASH algorithm within the Bluegenes tool.22 In this analysis, DLBCL cell lines were included. All DLBCL primary cases and cell lines are coded based on their cell-of-origin classification (ABC/GCB).39 (C) Hierarchical clustering of the same GC-derived B-NHL based on the expression of the “compound pathway signature,” as described in the main text. Note the presence of 2 main clusters (DZ-like, LZ-like). Red represents highly expressed genes; and blue, lower-expressed genes. The behavior of the signature in normal GC LZ/DZ B-cells is plotted in the accompanying heat map (left panel). DLBCL-PT indicates primary DLBCL cases; and DLBCL-CL, DLBCL cell lines.