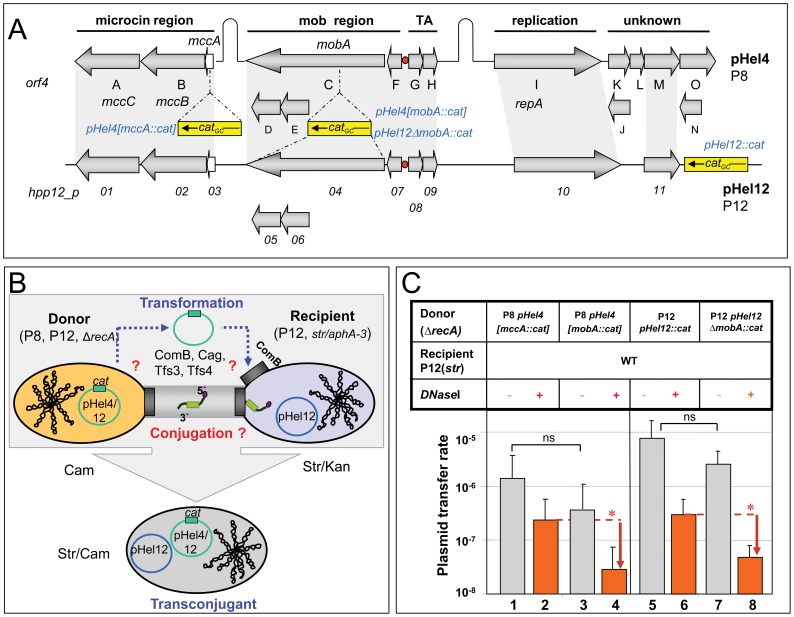
Figure 1. Structure of cryptic plasmids pHel4 and pHel12 and verification of their intra- and interstrain plasmid transfer.
(A) Schematic map showing the gene content and basic functional regions of two cryptic plasmids pHel4 and pHel12. Both plasmids contain a microcin gene cluster with homology to E. coli mccC7 (orf4A, B, X, or orf01, 02, 03). Genes orf4C-F and orf04-orf07, respectively, show homology to the mob region of colicinogenic plasmids. Genes orf4G/H and orf08/09, respectively, are related in sequence to the toxin-antitoxin system RelE-RelB (TA). The plasmid replicase is encoded by orf4I (pHel4) or orf10 (pHel12). Both plasmids also carry a number of hypothetical genes (orf4J-O, orf11). The insertion of the cat GC antibiotic resistance gene cassette into various orfs is shown. (B) Procedure of H. pylori co-cultivation to determine plasmid DNA transfer via natural transformation or conjugative processes. All T4SS (cag-PAI, comB, tfs3, tfs4) potentially involved in plasmid transfer between an H. pylori donor (P8, 12) and a recipient (P12) strain are indicated. Generally, natural transformation of the recipient strain by released plasmid DNA after lysis of the donor strain and conjugation processes are superimposed and are discriminated by adding of DNaseI. Plasmid transfer of pHel4[mccA::cat] or pHel12::cat from strain P8 or P12 into the P12 recipient strain was monitored by selection of the recipient strain (P12) via streptomycin (P12str) or kanamycin (P12moeB::aphA-3). To avoid the transfer of the chromosomal marker of the recipient (str, aphA-3) into the donor strain by natural transformation, the recA gene in the donor strain was deleted (P8ΔrecA::erm, P12ΔrecA::erm). (C) Inter- or intrastrain transfer of the cryptic plasmids pHel4[mccA::cat] or pHel12::cat from donor strain P8 or P12 into the recipient strain P12str in the absence (−) or presence (+) of DNaseI. Transfer rates were determined as the number of transconjugants/cfu/ml. Data shown are mean values of at least three independent experiments including standard deviations. * p<0.05, ns, not significant.