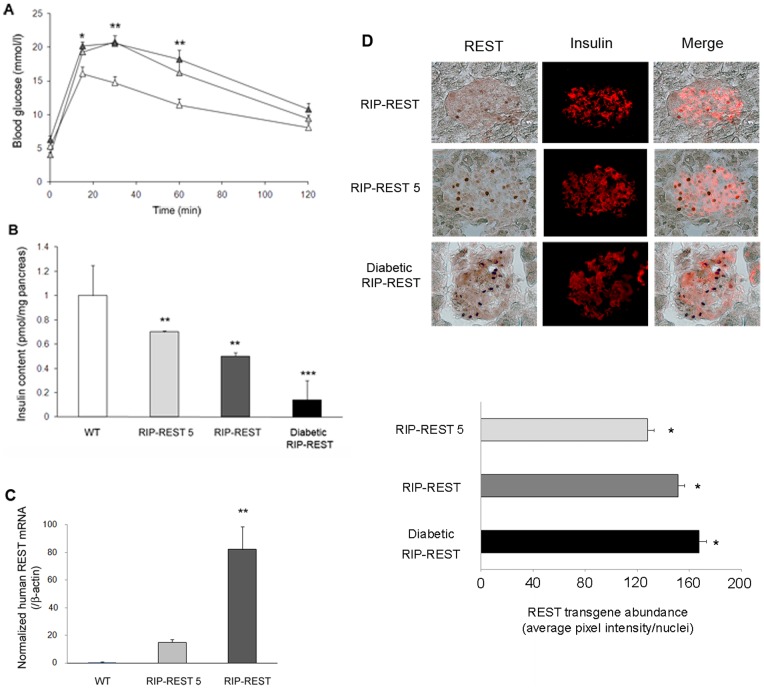
Figure 4. Increasing REST levels in beta cells lead to worsened glucose homeostasis.
A. Blood glucose levels in 6 month-old wild type (open triangles; n = 8), RIP-REST 5 (gray triangles; n = 8) and RIP-REST males (dark triangles; n = 10) during an IPGTT. After a 14 h fasting, blood samples were taken before (t = 0) and after (t = 15, 30, 60 and 120 min) intraperitoneal injection of glucose (2 g/kg). Results are mean ± SD. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. B. Insulin content in pancreas of 5 month-old RIP-REST 5 (light gray bar; n = 8), RIP-REST (dark gray bar; n = 6) and diabetic RIP-REST (black bar; n = 6) transgenic mice reveal a 30, 50 and 85% reduction, respectively, when compared with wild type mice (white bars, n = 6). Results are mean ± SD. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 versus values of wild type animals. C. Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of human REST mRNA levels in islets of 5 month-old WT (white bar; n = 5), RIP-REST 5 (light gray bar; n = 6) and RIP-REST (dark gray bar; n = 6) mice. REST mRNA levels are six-fold higher in RIP-REST than in RIP-REST 5 animals. Results are mean ± SD. **P<0.01 versus values of wild type animals. D. REST transgene abundance in islets from P2 RIP-REST 5, RIP-REST and diabetic RIP-REST mice. Upper panel shows representative images of REST protein levels revealed using specific antibodies against REST and AEC staining of peroxydase activity (nuclear black dots). Parallel immunostaining of insulin (red) and the merge shows colocalization of the two signals. Scale bar, 25 μm. Lower panel shows the quantification of the corresponding average pixel intensity per nuclei for each group. *P<0.05 versus the two other groups.