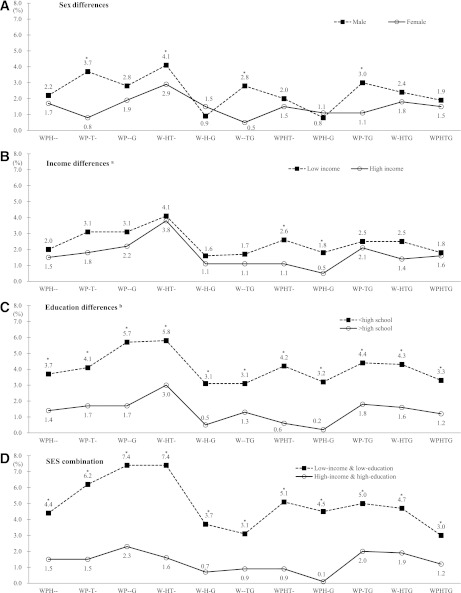
Figure 3.
Comparison of prevalence (%) of different combinations of MetS components by sex and SES among 19- to 65-year-old South Koreans: KNHANES 2007−2008. A: Male, ■; female, ○. B: Low income, ■; high income, ○. C: <HS, ■; >HS, ○. D: Low income and low education, ■; high income and high education, ○. G, blood glucose (hyperglycemia); H, HDL-C (low HDL-C); P, BP (hypertension); T, TG (hypertriglyceridemia); W, WC (central obesity). WPHTG, WC, BP, HDL-C, TG, and blood glucose. For example, WPHTG means that all MetS components (WC, BP, HDL-C, TG, and blood glucose) were included. W-HTG means that four groups (WC, HDL-C, TG, and blood glucose) were included and one MetS component (BP) was not included. aIncome was the quartiles of average household monthly income: low (Q1 + Q2), middle (Q3), and high (Q4). bEducation levels: <HS, HS, and >HS education. *P < 0.05, between-group difference was significant.