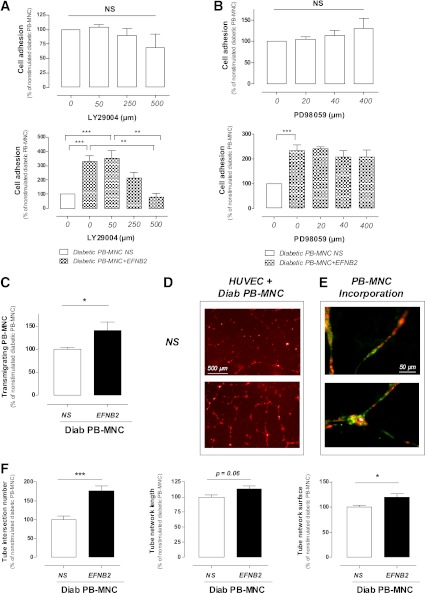
FIG. 5.
Effects of EFNB2 stimulation on diabetic PB-MNCs. A: Effects of specific inhibitor of PI 3-kinase signaling pathway (LY29004) on the adhesion of untreated (upper panel) (n = 4–10 per group) or pretreated (lower panel) (n = 5–10 per group) PB-MNCs from diabetic patients. B: Effects of specific inhibitor of MEK-1/2 signaling pathway (PD98059) on the adhesion ability of control (upper panel) (n = 5 per group) or pretreated (lower panel) (n = 5 per group) PB-MNCs from diabetic patients. C: Role of EFNB2 stimulation on the migration of PB-MNCs from diabetic patients (n = 12 per group). D: Representative images of capillary-like tube formation in cocultures of HUVECs and nonpretreated (upper panel) or pretreated (lower panel) diabetic PB-MNCs. E: Representative images of incorporated EFNB2-pretreated diabetic PB-MNCs (green) in the HUVEC network (red). F: Quantitative analysis of HUVEC network formation: intersection number, length, and surface (n = 9). NS, nonstimulated; Diab, diabetic. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. (A high-quality digital representation of this figure is available in the online issue.)