FIG. 6.
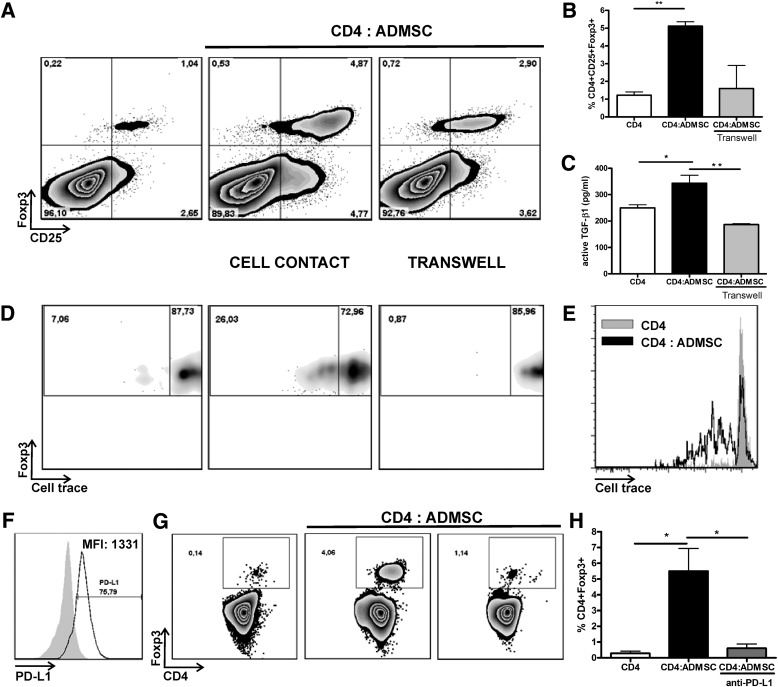
In vitro, ADMSCs promote the expansion/proliferation of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ T cells in a cell-to-cell contact-dependent manner in a mechanism mediated by PD-L1. A and B: In vitro expansion/proliferation of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ cells by ADMSCs. CD4+ T cells were isolated from the spleen of Foxp3-GFP C57BL/6 knock-in mice and cocultured together (cell-to-cell contact) or in a transwell system with ADMSCs (10 CD4+:1 ADMSC). The frequency of putative Tregs is shown as CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ cells in the CD4+ T-cell gate. C: Active TGF-β levels were quantified by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in the conditioned mediums and are shown as average ± SEM. D: CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ T-cell proliferation was verified using Cell Trace Violet staining. The percentage of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ divided cells after 4 days is shown by density plot representation. E: Histogram analysis showing the proliferation of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ T cells in the presence or absence of ADMSCs. F: PD-L1 expression by ADMSCs. Expression of PD-L1 was verified in ADMSCs by flow cytometry, and the frequency and median intensity of fluorescence (MFI) are shown. G: CD4+ T cells were cocultured with ADMSCs in the presence of anti-PD-L1 neutralizing antibody (clone 10F.9G2) or isotypic control. H: Frequency of CD4+Foxp3+ cells of three independent experiments is shown (average ± SEM). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.