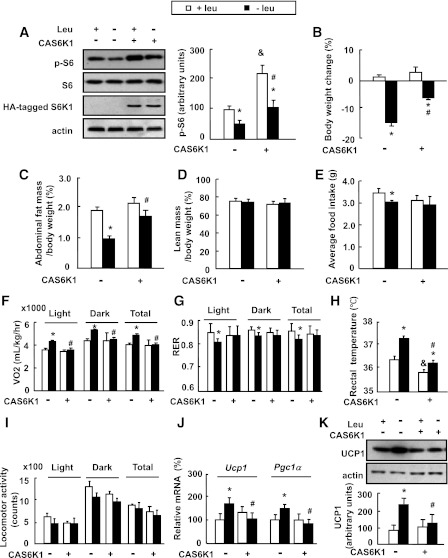
FIG. 2.
Intracerebroventricular injection of adenovirus expressing constitutively active S6K1 (Ad-CAS6K1) in the hypothalamus attenuates leucine deprivation–induced fat loss. Mice received intracerebroventricular injection of adenovirus expressing CAS6K1 (+CAS6K1) or GFP (−CAS6K1) and then were fed a control (+leu) or leucine-deficient (−leu) diet for 7 days. Energy expenditure was measured by indirect calorimetry. Data are means ± SEM of at least two independent experiments (n = 6 for each group). Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA followed by the SNK test. *P < 0.05, for the effect of −leu vs. control diet within the same intracerebroventricular group; #P < 0.01, for the effect of with vs. without Ad-CAS6K1 under −leu diet; &P < 0.01, for the effect of with vs. without Ad-CAS6K1 under control diet. A: Hypothalamic HA-tagged S6K1 and S6 proteins (left, Western blot; right, quantitative measurements of p-S6 protein relative to total S6). B: Body weight change. C: Adipose tissue mass in proportion to body weight. D: Lean mass in proportion to body weight. E: Average food intake. F: Oxygen consumption (VO2; 24 h). G: RER. H: Rectal temperature. I: Physical activity. J: Ucp1 and Pgc-1α mRNA in BAT. K: UCP1 protein in BAT (top, Western blot; bottom, quantitative measurements of UCP1 protein relative to actin).