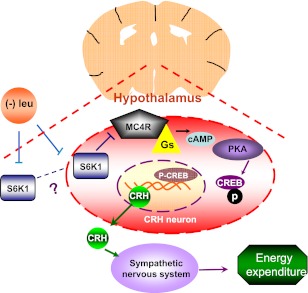
FIG. 7.
Hypothalamic S6K1 regulates energy expenditure via MC4R-dependent modulation of CRH under leucine deprivation. Dietary leucine deprivation inhibits hypothalamic S6K1 activity, which in turn increases the G protein–coupled, seven-transmembrane receptor MC4R protein levels and stimulates Gs activity. These events increase intracellular cAMP levels, which stimulates cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA)–mediated phosphorylation and activation of CREB. In the nucleus, Crh transcription is stimulated by the binding of phosphorylated CREB at the cAMP-responsive element site in its promoter. After translation and modification, CRH is secreted as a polypeptide and activates the sympathetic nervous system to stimulate energy expenditure and thermogenesis in the whole organism.