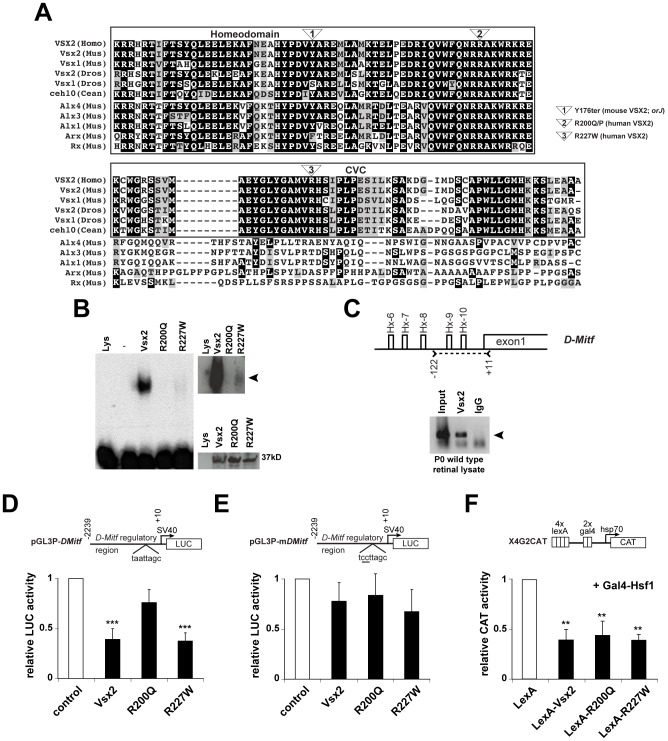
Figure 1. DNA binding and transcriptional activities of VSX2 and the VSX2[R200Q] and VSX2[R227W] variants.
(A) ClustalW alignment of the homeodomain and adjacent 60 amino acids in select VSX orthologs and the most similar non-VSX proteins in mice. Only the VSX sequences have a discernable CVC domain. The positions of the orJ, R200Q, and R227W mutations are shown. (B) Left panel: EMSA with in vitro translated VSX2, VSX2[R200Q], and VSX2[R227W] proteins and [32]P-labeled P3 oligo (see Table S1 for sequence). Top right panel: Extended exposure reveals weak binding by VSX2[R227W]. Bottom right panel: Western blot of in vitro translated proteins with VSX2 antibody (Lys, control lysate; -, P3 probe only). (C) Schematic shows five putative Vsx2 binding sites (Hx-6 – Hx-10) in the proximal promoter region (∼0.3 kb) of D-Mitf. Carats and dashed line marks the region of PCR amplification in the ChIP assay shown below schematic (primer set 13; Table S1). Arrowhead points to sequence-verified ChIP product. (D) Luciferase assays in P0 primary retinal cells transfected with the indicated expression vectors (x-axis) and ∼2.2 kb of the D-Mitf promoter region (pGL3P-DMitf). (E) The Hx-9 site was mutated in pGL3P-mDMitf to eliminate DNA binding at that site. Reporter assays were normalized to empty vector controls (white bars). (F) CAT assays in HEK293 cells transfected with the X4G2CAT reporter and VSX2 variants fused to the LexA DNA binding domain. Gal4-Hsf1 was included to stimulate high basal reporter activity [34]. ** P≤0.01; *** P≤0.001.