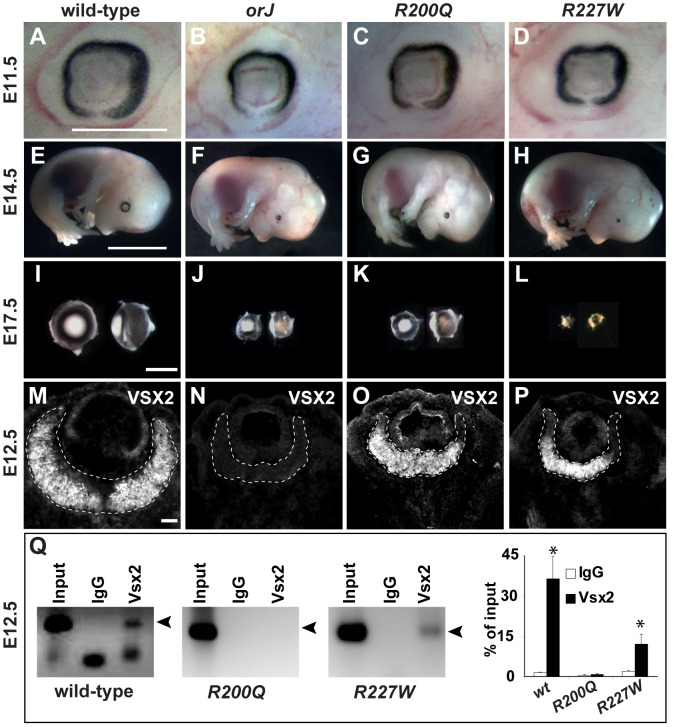
Figure 2. The R200Q and R227W mutations cause non-syndromic congenital microphthalmia.
(A–D) Mice homozygous for the orJ, R200Q, and R227W alleles had smaller eyes than wild-type by E11.5. (E–H) At E14.5, overall embryonic development was unaffected in the mutants, but the failure of the mutant eyes to keep pace with the growth of the wild-type eye was evident. Eye growth in the R227W mutant also failed to keep pace with the orJ and R200Q mutants. (I–L) Dissected E17.5 eyes (right eyes rotated 90°) show similar reductions in eye size in orJ and R200Q homozygotes whereas the reduction in eye size of R227W homozygotes was the most severe. (M–P) VSX2 immunohistochemistry in E12.5 retinas. VSX2 protein was not detected in the orJ retina, confirming it as an expression null. VSX2[R200Q] and VSX2[R227W] were expressed similarly to VSX2[wt], although to a reduced extent in peripheral retina. Dashed lines bound retinas. (Q) ChIP assays with VSX2 antibody reacted with E12.5 native chromatin lysates from wild-type, R200Q, and R227W retinas and amplified using D-Mitf primer set 13 (Table S1). Arrowhead denotes amplification product. Graph shows quantification results of ChIP-qPCR. Scale bars: 0.5 mm (E11.5); 5 mm (E14.5); 1 mm (E17.5).