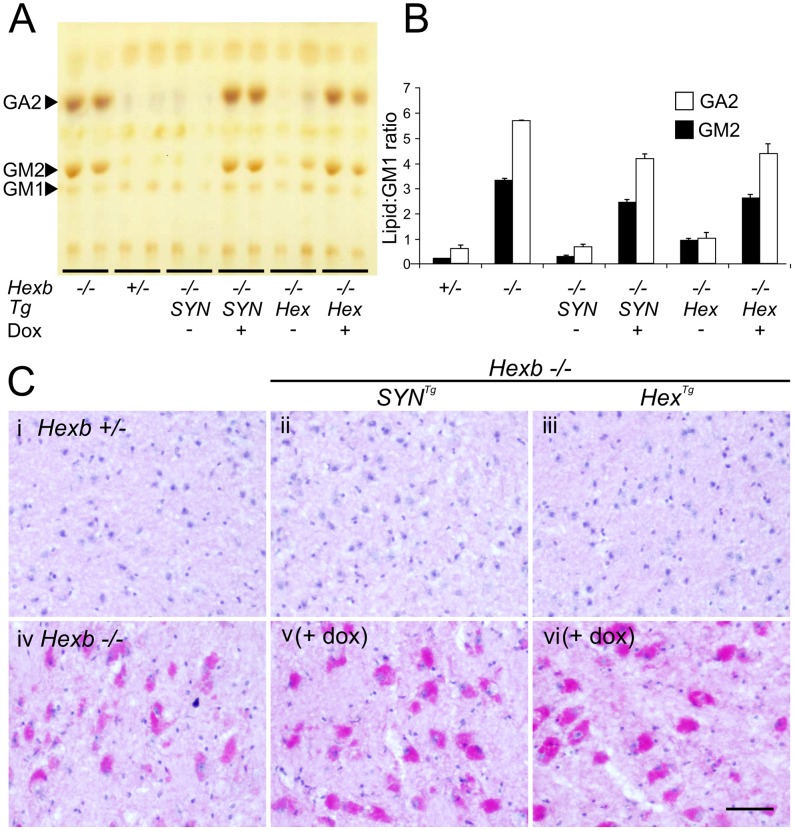
Figure 7. Doxycycline mediated silencing of transgenic Hexb expression induces storage of glycolipids.
(A and B) Thin layer chromatography shows increase in the amount of GA2 and GM2 lipid in extracts of Sandhoff mouse cerebrum that were taken at the humane endpoint. Only trace amounts of the same lipids exist in age-matched heterozygous controls. Both SYN and Hex transgenic constructs prevented the accumulation of GM2 and GA2 in the Sandhoff mouse at approximately six months of age. When Hexb−/−HexTg or Hexb−/−SYNTg mice were fed doxycycline from five weeks of age until their humane endpoint, these lipids accumulated to amounts seen in the Sandhoff mouse at humane endpoint (n = 4, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4, for Hexb+/−, Hexb−/−, Hexb−/−SYNTg (−Dox) and (+Dox), Hexb−/−HexTg (−Dox) and (+Dox), respectively). (C) PAS staining in the thalamus shows weak staining in the Hexb+/− animal (i) and strong staining in neurons of the Sandhoff animal at humane endpoint (iv, magenta staining). Hexb−/−HexTg and Hexb−/−SYNTg animals were protected from accumulation of lipids in the thalamus, shown by a lack of PAS staining (ii and iii). In animals that were fed doxycycline, PAS staining revealed significant accumulation of glycoconjugates (v and vi). Sections were counterstained with haematoxylin. Scale bar = 50 µm.