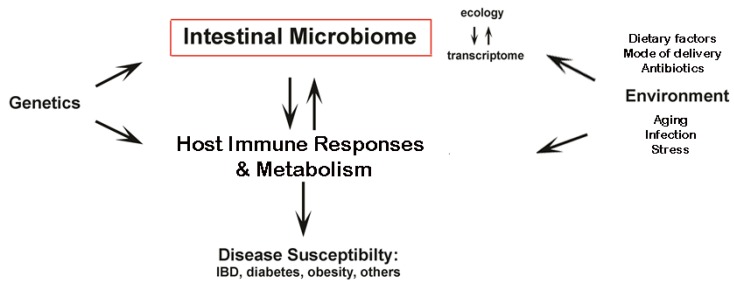
Figure 1.
Diet-induced dysbiosis affects disease susceptibility. The intestinal microbiome (microbial ecology and their genetic material) is influenced by both host genetics and the environment including dietary factors. In diseases including IBD, diabetes and obesity, diet is implicated as a contributing factor by having direct effects on host metabolism and/or immune responses. However, recent evidence suggests that diet also influences the composition of the microbiome. This could, in turn, affect host immunity and metabolism and alter susceptibility to disease.