Figure 2.
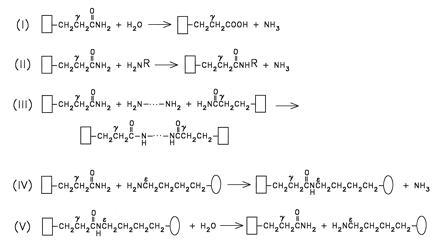
Reactions catalyzed by transglutaminases. The backbones of protein or peptide substrates, carrying TG-reactive Gln (i.e., acceptor) and Lys (i.e., donor) side chains, are illustrated by open rectangles and ovals, respectively. Reactions RI and RV reflect on the hydrolytic nature of this group of enzymes (for the isopeptide hydrolyzing activities indicated in V, see ref. 58). Transamidating possibilities are shown in reactions II–IV. Geometry of crosslinked products, as formed in reaction IV, depends on the number and spatial distribution of TG-reactive Gln and Lys residues in the acceptor and donor protein substrates (3). Synthetic, small molecular weight primary amines (H2NR, reaction II, e.g., glycine ethylester or dansylcadaverine) are frequently used to inhibit protein-to-protein crosslinking events by blocking the TG-reactive Gln residues.
