Figure 1. Excessive post-injury T-cell apoptosis that presage the development of T-cell anergy is TRAIL-induced.
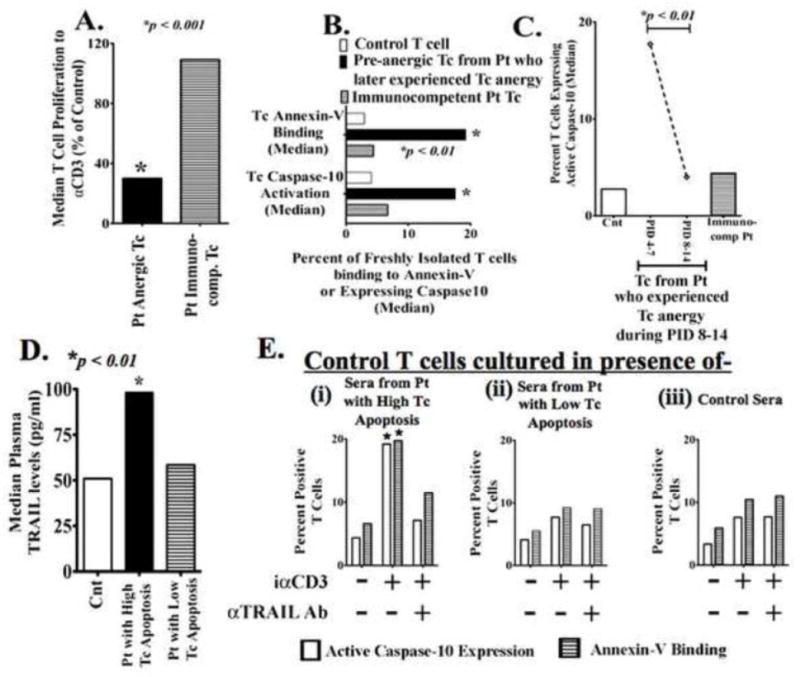
(A) Freshly isolated T-cells from trauma patients (Pt) and age, sex and ethnicity matched controls (Cnt) were stimulated with plate-bound αCD3 to assess T-cell (Tc) proliferation. Pt T-cells were considered anergic when proliferation to αCD3 was less than 50% of Cnt T-cell response. Data show the median value from 17 Pt with T-cell anergy and 96 immunocompetent Pt; p<0.001 by t test and ANOVA. (B) Trauma patients who experienced T-cell hyporesponsiveness showed earlier pre-anergy elevated T-cell apoptosis. Freshly isolated Patients’ (Pt) and matched Controls’ (Cnt) T-cells were incubated with annexin-V + 7AAD or FAM-AEVD-FMK peptides (binds specifically to human active Caspase-10) and assayed by flowcytometry. Data shows the median value. *p<0.01 by t test and ANOVA compared to controls’ and immunocompetent patients’ T-cells. (C) Only Pt with early (PID- 4–7) excessive T-cell apoptosis later (PID- 8–14) developed T-cell anergy. Pt actual anergic T-cell (PID- 8–14) did not show increased apoptosis. *p<0.01 by t test and ANOVA. (D) Patients experiencing increased T-cell apoptosis also had increased plasma TRAIL levels as determined by ELISA *p<0.01 by Mann-Whitney U test compared to matched controls. (E) Freshly isolated control T-cells were stimulated with iαCD3 in culture with IMDM medium plus (i) sera from Pt who experienced elevated T-cell apoptosis, (ii) sera from Pt with low T-cell apoptosis, or (iii) sera from matched healthy control volunteers. In the indicated experimental conditions, sera were pre-treated with αTRAIL blocking antibody to block existing TRAIL in the sera. After 5 days of culture, T-cell Caspase-10 activation and annexin-V binding were assessed n=3 for each Pt group; n=6 for Cnt *p < 0.05.
