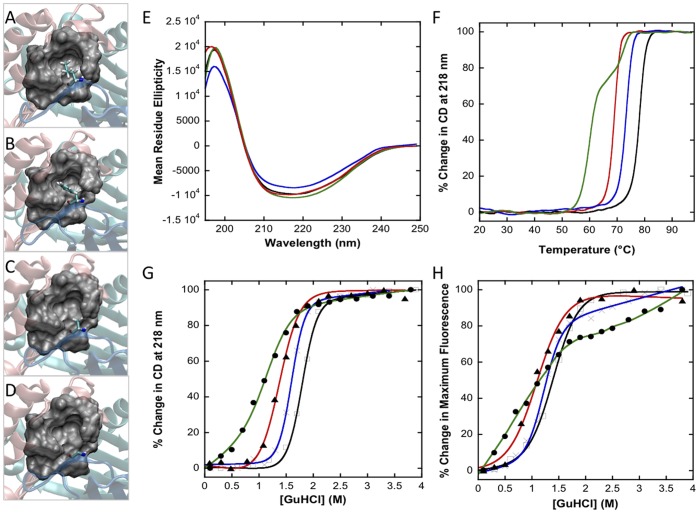
Figure 2. Disrupting the hydrophobic interactions via mutating Leu46 alters the structural stability of MIF.
(A) Leu46 hydrophobic pocket of wt huMIF. VMD representations of the hydrophobic pocket, where Leu46 is mutated to a phenylalanine (L46F) (B), alanine (L46A) (C), or glycine (L46G) (D). (E-H): The three Leu46 mutants are structurally less stable than the wild type protein, but retain the same overall secondary structure. (E) Far-UV CD spectra of wt and Leu46 mutants. (F) Thermal denaturation of wt and Leu46 mutants (at 20 µM) followed by far-UV CD at 218 nm. (G) GdnHCl denaturation studies monitored by far-UV CD at 218 nm and fluorescence spectroscopy (H), excitation wavelength: 295 nm, protein concentration: 10 µM. All spectroscopic experiments were performed in PBS 1X, pH 7.4 buffer. Black lines, wt MIF; blue lines, L46F MIF; red lines, L46A MIF; green lines: L46G MIF.