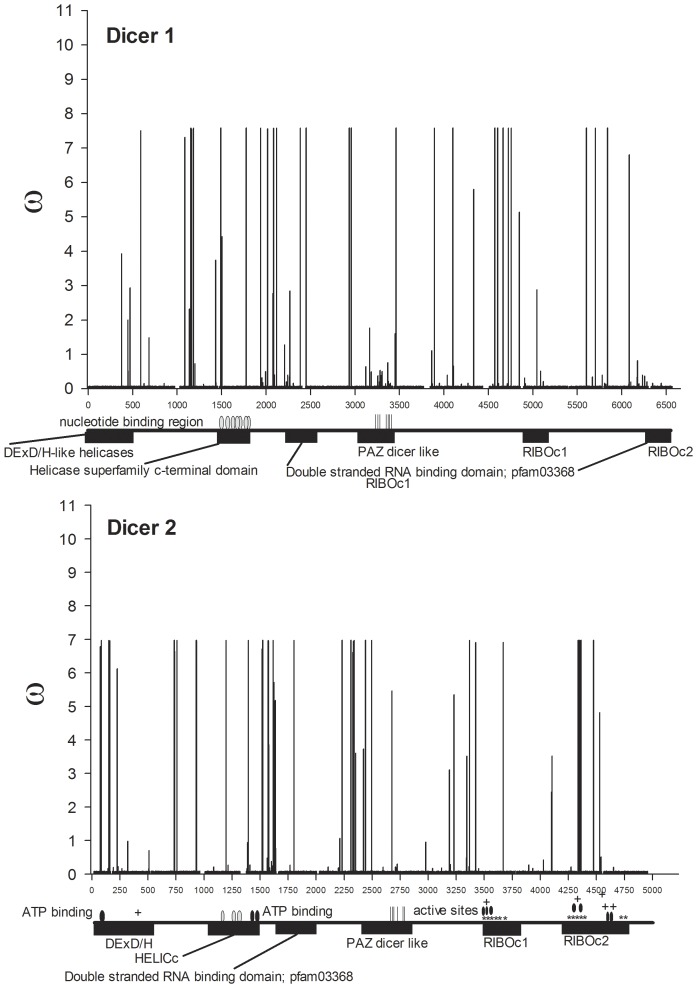
Figure 4. w ratios for all nucleotides mapped across annotated Dicer genes.
The amino-terminal domains of most Dicer enzymes contain a DExH-box RNA or ERCC4-like helicase domain followed by members of helicase superfamily c-terminal domains containing a number of nucleotide binding regions (gray ovals) and an ATP binding domain on Dcr 2 (black ovals). One or two double stranded RNA-binding domains (dsRBDs) consisting of ∼100 amino acid residues occur in the center and the carboxyl end of Dicers. The first of these dsRBDs is followed by the oligonucleotide-binding (indicated with vertical lines) PAZ domain located in the center of Dicer where it binds the 5′ phosphates and 2 nt 3′ hydroxyl overhangs. Cleavage is accomplished by dimerized RNase III domains (labeled RIBOc). Active sites (black ovals) are shown on Dcr2. The areas of dimerization are labeled with ‘*’ while regions of metal ion-binding are labeled with a ‘+.’