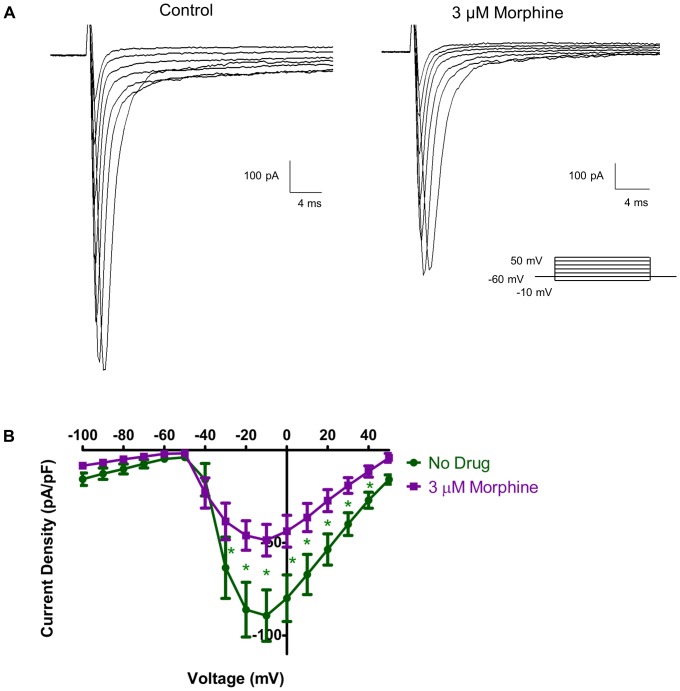
Figure 8. Morphine inhibits Na+ channel current.
During voltage clamp recordings (A), Na+ channel current is seen as a quick inward spike in response to depolarizing steps in absence of drug (A, left panel). Cs+ has been added to the internal solution to block all confounding K+ current. In the presence of 3 µM morphine (A, right panel), the amplitude of Na+ channel currents is reduced. A current density-voltage relationship (B) shows that morphine (3 µM) significantly inhibits Na+ flow. Significance is determined via two-way ANOVA (n = 8, * = p<0.05).