Figure 6.
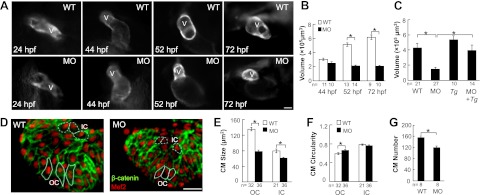
Injection of actn2 MO leads to reduced size of the ventricular chamber and individual CMs. A) Ventricle enlargement is halted by actn ctn2 MO. Images show individual fish hearts from living Tg(ttna:megfp) fish embryos with or without actn2 MO injection. Dorsal view and ventral view with the head facing up is shown for embryos at 24 and 44 hpf, respectively; embryos at 52 and 72 hpf are shown in lateral views with the head to the left. V, ventricle. B) Quantification of ventricular volume reveals a significantly reduced ventricular chamber size in MO fish at both 52 and 72 hpf. C) Reduced ventricular chamber sizes in MO fish can be rescued by Tg(ttna:actn2-egfp). D) Image of a ventricle after immunostaining with Mef2 (red) and β-catenin (green) to define the nuclei and the outline of the CMs. Typical OC and IC cells are encircled with solid and dashed lines, respectively. E, F) Quantification of CM size and circularity shows that CM size is significantly reduced in both the OC and IC regions, while CM circularity is only increased in the OC region. G) CM number in the ventricle is reduced in actn2 morphant fish. MO, fish injected with actn2 MO; Tg, Tg(ttna:actn2-egfp) fish; MO+Tg, Tg(ttna:actn2-egfp) fish injected with actn2 MO, OC, outer curvature; IC, inner curvature; n, number of fish (B, C, G) or CMs (E, F). Scale bars =20 μm (A); 40 μm (D). *P < 0.05.