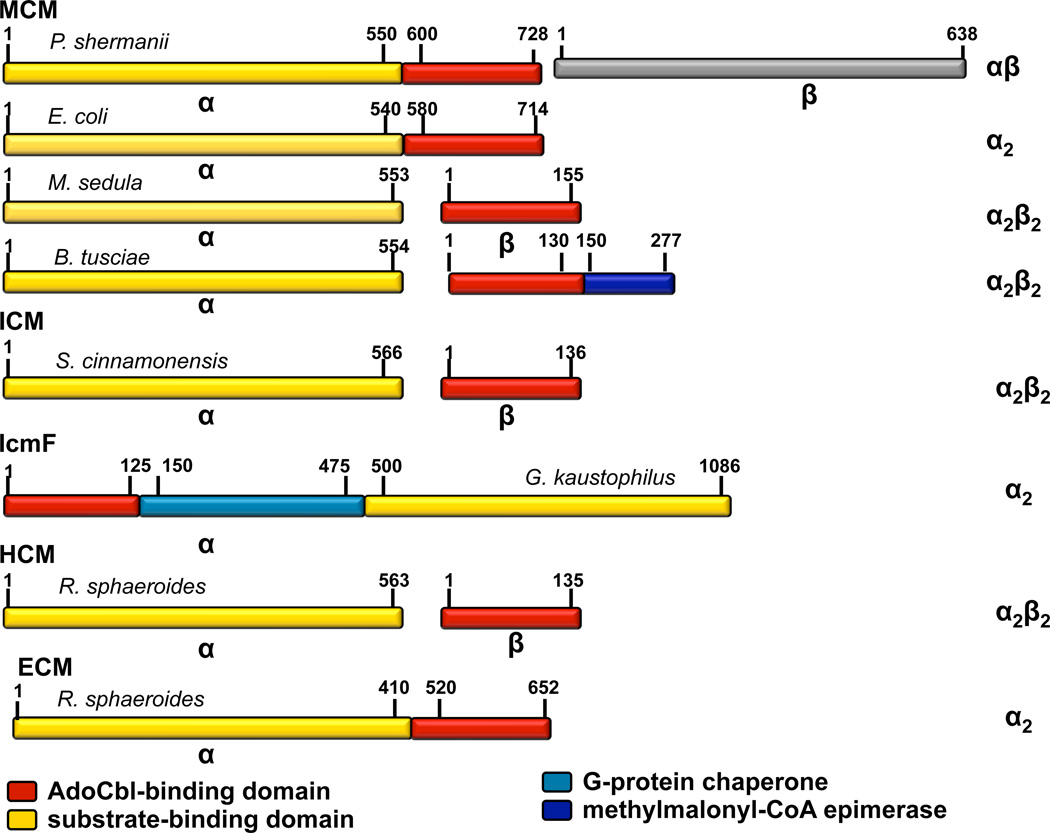
Figure 2.
Domain organization of acyl-CoA mutases. The domains/subunits are color-coded as follows: AdoCbl-binding domain (red), substrate-binding domain (yellow), methylmalonyl-CoA epimerase (navy) and G-protein chaperone (cyan). The oligomeric state of the proteins is shown on the right. The following proteins were used as examples: MCMs (Propionibacterium shermanii (αβ)(P11653, P11652), E. coli (α2)(AAA69084), Metallosphaera sedula (α2β2)(Msed_0638, Msed_2055) and Bacillus tusciae (α2β2)(YP_003589181)); ICM (Streptomyces cinnamonensis (α2β2)(AAC08713, CAB59633)), IcmF (Geobacillus kaustophilus (α2)(YP_149244)), HCM (Rhodobacter sphaeroides (α2β2)(Rsph17029_3657, Rsph17029_3654)), and ECM (Rhodobacter sphaeroides (α2)(ACJ71670)).