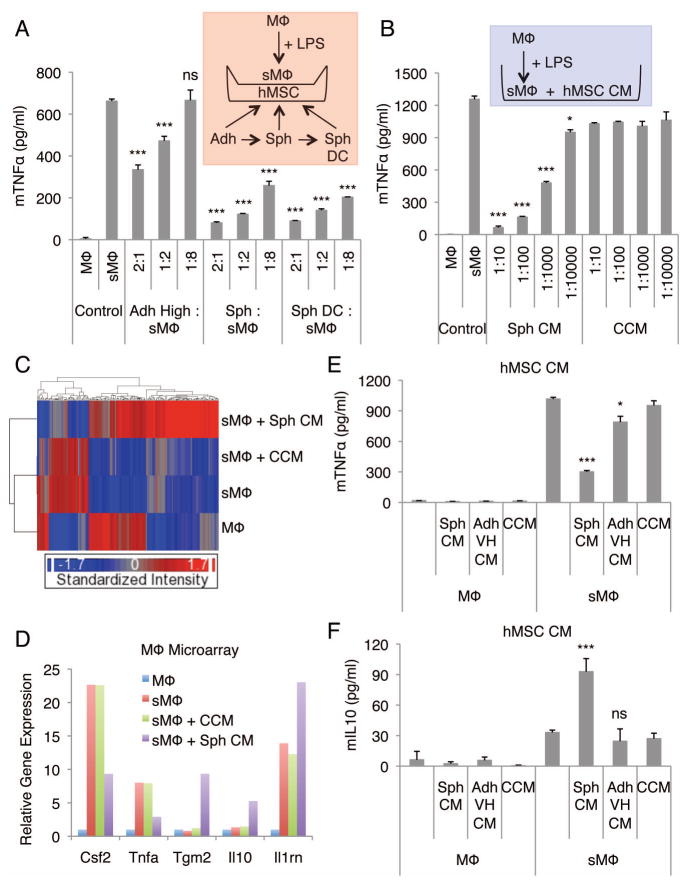
Figure 1. hMSC spheroids and spheroid-conditioned medium promote anti-inflammatory macrophage phenotype.
(A) hMSC spheroids and spheroid-derived cells reduce the secretion of mTNFα by LPS-stimulated macrophages. Transwell co-cultures of macrophages and hMSCs at different cell ratios. (B) hMSC spheroid-conditioned medium reduces the secretion of mTNFα by LPS-stimulated macrophages at a dose-dependent manner. (C) Hierarchical clustering of mouse macrophage microarray data. (D) Relative gene expression levels of selected inflammatory related genes from the mouse macrophage microarray data. Un-stimulated mouse macrophages were used as a baseline. (E,F) Comparison of the spheroid and monolayer hMSC conditioned medium effect in production of mTNFα (E) and mIL10 (F) by LPS-stimulated macrophages. Values are mean ± SD (n = 3). ns P ≥ 0.05, *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001 compared to control (sMΦ) in A, compared to corresponding vehicle controls (CCM) in B, and compared to vehicle control (CCM) in E and F. Abbreviations: Adh High, adherent monolayer hMSCs plated at high density (5,000 cells/cm2) and cultured for 3 d; Adh VH, adherent monolayer hMSCs plated at very high density (200,000 cells/cm2) and cultured for 3 d; CM, conditioned medium; CCM, complete culture medium; hMSC, human mesenchymal stem/stromal cell; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; mTNFα, mouse TNFα; MΦ, macrophage; sMΦ, stimulated macrophage; Sph, spheroid hMSC from 3 d hanging drop cultures (25,000 cells/drop); Sph DC, spheroid-derived cell.