Figure 1.
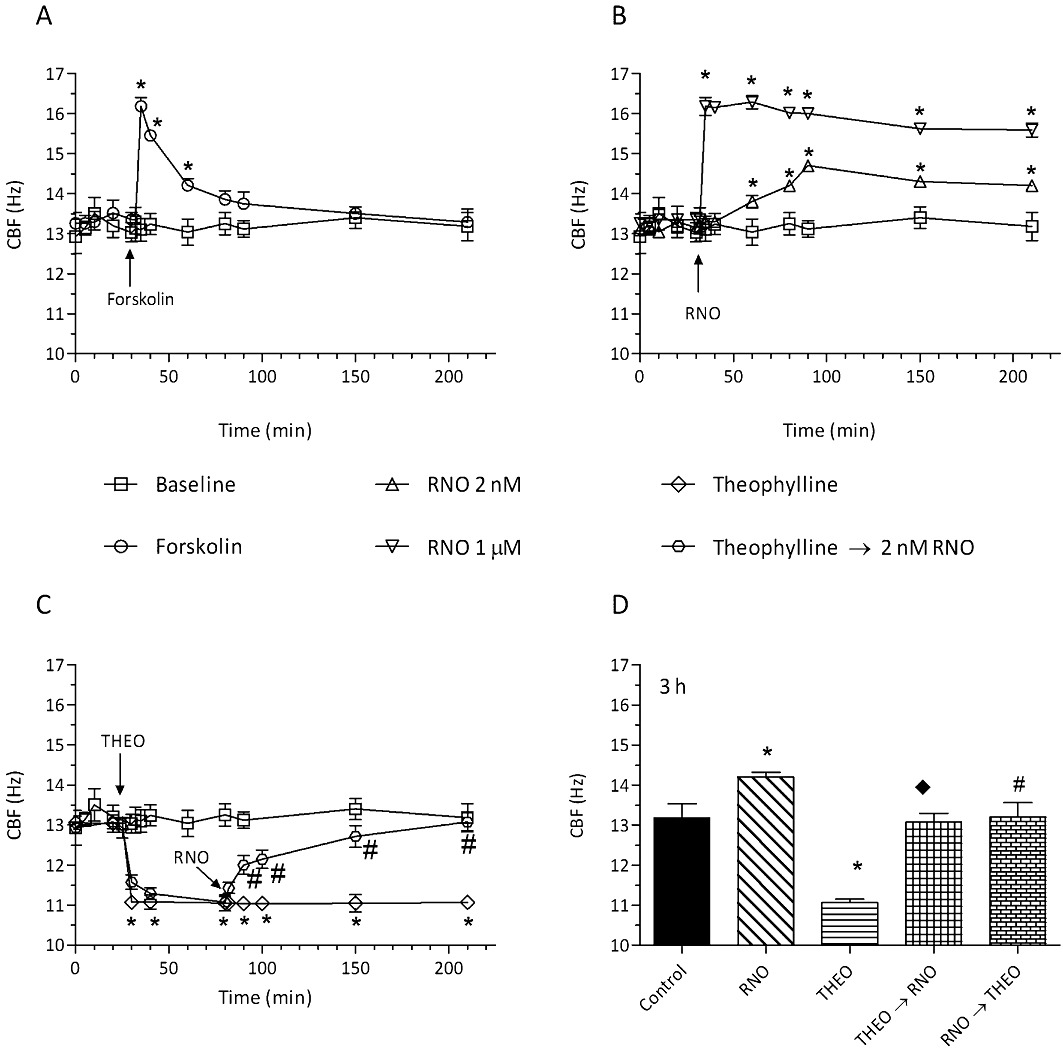
Forskolin and roflumilast N-oxide rapidly increased CBF of differentiated human bronchial epithelial cells, effects of theophylline. Following an initial 20 min baseline period, differentiated bronchial epithelial cells (D-BECs) were incubated with forskolin at 10 µM (A), or roflumilast N-oxide (RNO) at 2 nM or 1 µM (B), or theophylline (THEO) at 10 µM followed by roflumilast N-oxide (2 nM) (C) or vehicle (baseline), and ciliary beat frequency (CBF) was monitored for up to 3 h. (D) D-BECs were incubated with vehicle (control), or 2 nM RNO, or THEO at 10 µM, or THEO followed by RNO (from 80 min) (THEO→RNO), or RNO followed by THEO (from 80 min) (RNO→THEO), and the CBF assessed at 3 h is depicted. CBF was measured by DHSV microscopy and quantified by Fourier transformation as detailed in Methods. Results are shown as the means ± SEM of three experiments per donor based on cultures from two to four different donors per condition. Vehicle (0.1% DMSO for RNO or forskolin and 10 µM HCl for THEO) was included in the controls and did not affect CBF over the observation period. (A and B) *P < 0.05 versus baseline. (C) *P < 0.05 versus baseline; #P < 0.05 versus THEO. (D) *P < 0.05 versus control; #P < 0.05 versus RNO; ◆P < 0.05 versus THEO.
