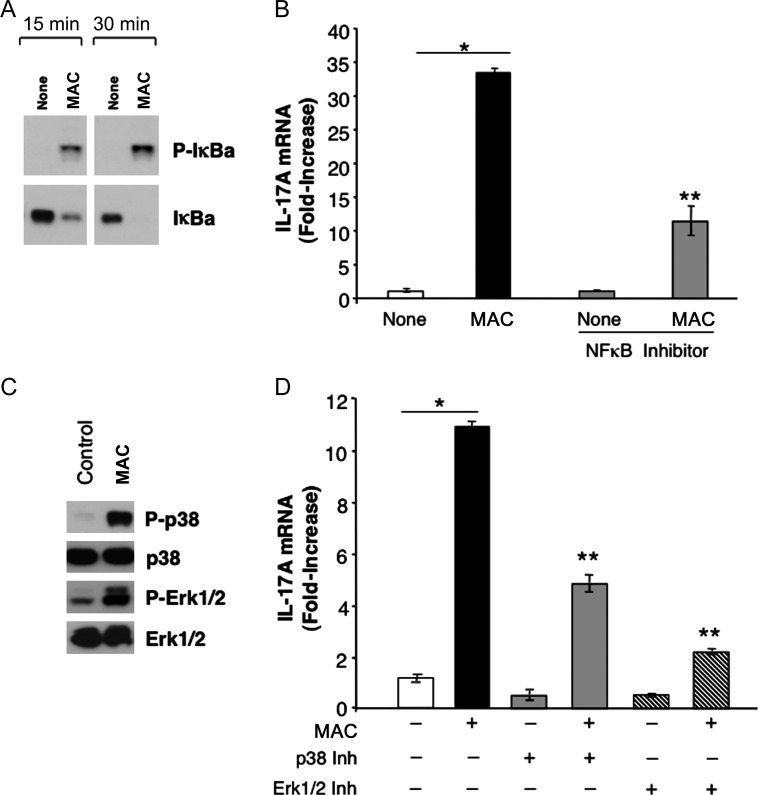
Figure 5.
Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC)–induced interleukin 17 (IL-17) is mediated by NF-κB and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways. A, Human macrophages were incubated with MAC, and whole protein cell lysates were generated after 15 and 30 minutes and examined for P-IκB activation and IκB by Western blot. B, Preexposure of macrophages to the NF-κB inhibitor Bay-11-7082 (for 1 hour) suppressed MAC-induced IL-17A, as shown by real-time polymerase chain reaction (*P < .01 for no exposure vs MAC exposure, **P < .05 for both MAC and inhibitor exposure vs MAC-only exposure; n = 3). C, Whole protein cell lysates (30 minutes) from unexposed and MAC-exposed macrophages were analyzed for phosphorylation of p38 and Erk1/2 MAPK and total MAPK (n = 3). D, IL-17 mRNA expression in macrophage cultures preexposed to a p38 or Erk1/Erk2 MAPK inhibitor for 1 hour prior to exposure to MAC for 4 hours (*P < .01 for no exposure vs MAC-only exposure, **P ≤ .01 for both MAC and inhibitor exposure vs MAC-only exposure; n = 3). Representative donor data are shown.